山药(Chinese yam,CY)又称薯蓣、土薯、薯药等,为薯蓣科 (Dioscoreaceae) 薯蓣属(Dioscorea L.)植物薯蓣(Dioscoreaopposita Thunb.)[1]。我国是山药的原产地,自夏、商开始种植[2],目前形成东北、华北、西北、华中华东、华南5 个产区,其中河南省种植面积达到7 万hm2[3]。山药味甘性平,归脾、肺、肾经[4],主要功能成分包括多糖、多酚类化合物、皂苷、尿囊素等[5-6]。本文根据近5年研究,综述山药组成成分的理化性质,功能活性及作用机制,并预测其应用前景,为其作为药食同源性食品的研究提供理论依据。
1 山药主要活性成分研究
山药营养物质丰富,以古怀庆者(今河南焦作)最佳。如表1所示,以铁棍山药和普通山药为例,显示其营养成分的占比[7]。山药中活性物质有多糖、多酚、磷脂、山药素(I、II、III、Ⅳ、V)、盐酸山药碱、槭素Ⅱ、多酚氧化酶等,包括皂苷、尿囊素、多巴胺、胆甾醇、β 谷甾醇、麦角甾醇、菜油甾醇等多种有机化合物,另外含有维生素C、微量元素I、Ca、Fe、P[3,8-9]。
表1 山药的主要营养组成(%)
Table 1 Main nutrient composition of Chinese yam(%)

?
近年来,国内外的研究主要集中在多糖、多酚、薯蓣皂苷、尿囊素等物质上,这些化学成分决定山药的营养价值和作用活性。山药多糖(Chinese yam polysaccharide,CYP)的干粉含量约为7.4%~13.5%[10],主要由甘露糖、阿拉伯糖、木糖、葡萄糖、半乳糖及少量岩藻糖组成[11]。其组分随提取条件的不同存在差异,低温浸提得到的多糖主要由甘露糖组成,高温煎煮得到的多糖主要由葡萄糖组成[12]。山药多糖具有增强体液免疫、抗氧化、抗肿瘤、调节胃肠道、降血糖等多种功能。
多酚是山药中重要的抗氧化物质,含量约为0.08%~0.11%[13-14]。研究发现,总酚含量由多至少依次为白肉山药>红肉山药>黄肉山药,而且肉色越深山药的总酚化合物含量越高。由于总酚由类黄酮、酚酸和单宁这3 种酚类化合物构成,研究山药生长中多酚含量变化,发现类黄酮是最主要的酚类物质,占到六成以上,主要由花青素和黄酮醇构成[15]。紫山药(Dioscoreaalata)的肉质部和表皮均含有较多类黄酮化合物等酚类抗氧化物质,并且山药皮中含量较高[16]。
薯蓣皂苷(Diosgenin,DG)由螺甾烷型的薯蓣皂苷元和糖链以糖苷键相连,分子结构如图1所示,在山药干粉中占0.6%~1.0%[17],在皮中含量最高[18]。近年来,关于薯蓣皂苷的功能性研究主要集中在调节免疫、抗肿瘤、抗炎镇痛、保护胃肠黏膜等方面。此外,在山药小分子活性成分的研究领域,以尿囊素(Allantoin)、胆碱(Choline)的研究居多[5]。尿囊素是咪唑类化合物,分子式为C4H6N4O3,分子结构如图1所示。尿囊素是山药主要的有效成分之一,占比在0.9%~1.0%之间,其含量在山药及其产品的质量评价上起着重要指标作用[17]。

图1 山药活性物质(薯蓣皂苷和尿囊素)的分子结构
Fig.1 Molecular structures of Chinese yam active constituents (diosgenin and allantoin)
2 山药的营养功能研究
山药气味平和,温补而不骤,微香而不燥,是中医常用的一味健脾补气良药[19]。关于山药营养功效始载于《神农本草经》,称“能补虚赢,益气力,久服耳目聪明,轻身延年”。《本草纲目》将其概括为“益肾气,健脾胃,止泄痢,化痰涎,润皮”五大功用[5]。
2.1 调节免疫
如表2所示,CYP 可提高T 淋巴细胞增殖能力和 NK 细胞活性,同时促进白细胞介素2(Interleukin-2,IL-2)、肿瘤坏死因子(Tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α)、干扰素-γ(Interferonγ,IFN-γ)、主要组织相容性复合体(Major histocompatibility complex,MHC)水平升高[20-23]。除了增强体液免疫,CYP 还能促进吞噬细胞向M1型极化,激活其吞噬能力,增强细胞免疫功能[24],其中作用机制包括调节Toll 样受体4 (Toll like receptor 4,TLR4)-核因子κB(Nuclear factor κB,NFκB),促进细胞外信号调节蛋白激酶(Extracellular -signal regulated protein kinase,ERK)、c-Jun N 末端蛋白激酶(c-Jun N-terminal kinase,JNK)、p38 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase,p38) 磷酸化,激活丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(Mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)途径[25]。除此之外,可以缓解卡介苗和脂多糖 (Lipopolysaccharide,LPS) 诱导的肝指数、脾指数降低[26]。
表2 山药免疫功能研究现状
Table 2 Research status of immune function of Chinese yam
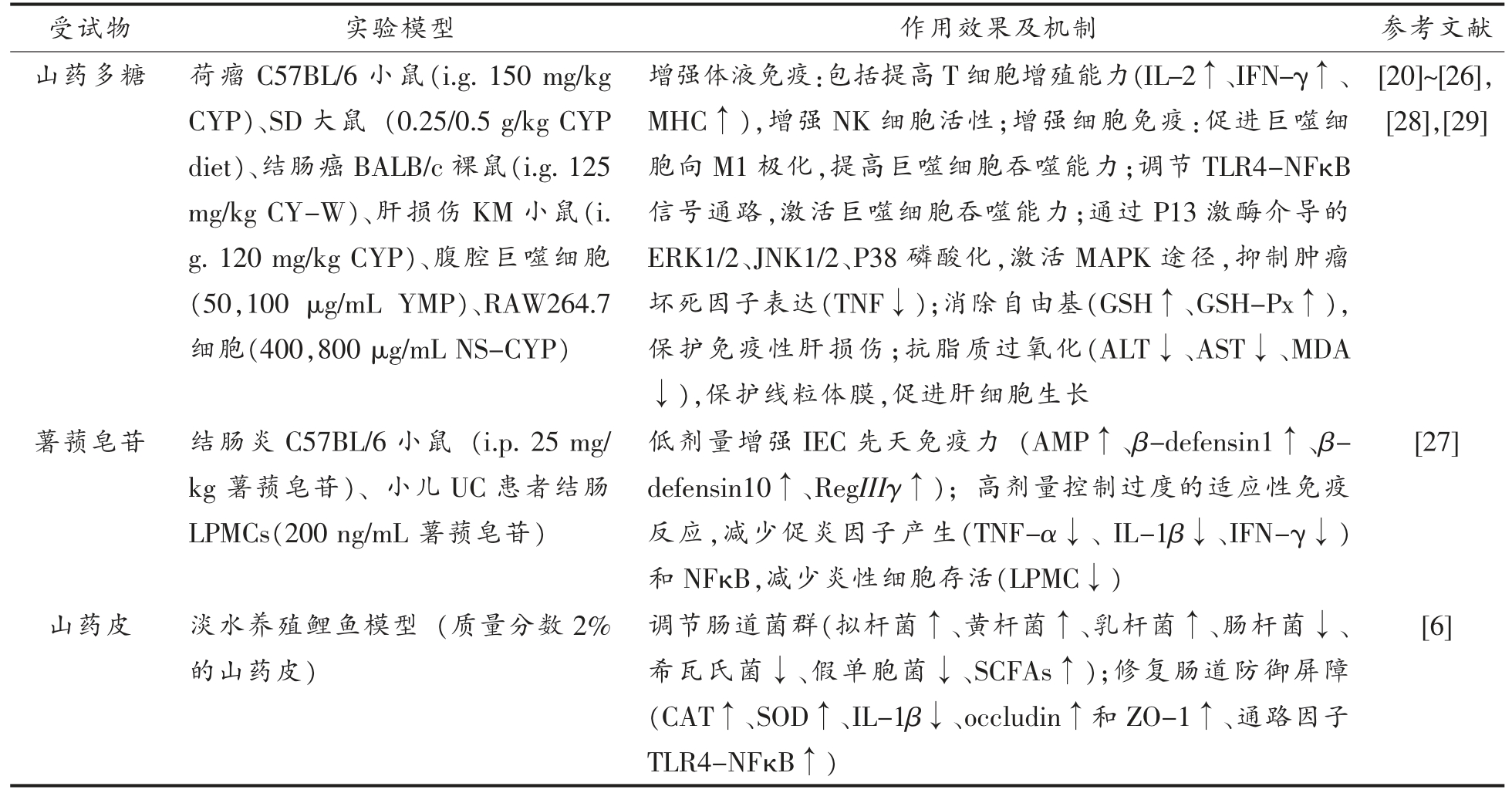
注:YMP.山药黏多糖;CY-W.山药水提取物;NS-CYP.非淀粉多糖。
受试物 实验模型 作用效果及机制 参考文献山药多糖 荷瘤C57BL/6 小鼠(i.g.150 mg/kg CYP)、SD 大鼠 (0.25/0.5 g/kg CYP diet)、结肠癌BALB/c 裸鼠(i.g.125 mg/kg CY-W)、肝损伤KM 小鼠(i.g.120 mg/kg CYP)、腹腔巨噬细胞(50,100 μg/mL YMP)、RAW264.7细胞(400,800 μg/mL NS-CYP)增强体液免疫:包括提高T 细胞增殖能力(IL-2↑、IFN-γ↑、MHC↑),增强NK 细胞活性;增强细胞免疫:促进巨噬细胞向M1 极化,提高巨噬细胞吞噬能力;调节TLR4-NFκB信号通路,激活巨噬细胞吞噬能力;通过P13 激酶介导的ERK1/2、JNK1/2、P38 磷酸化,激活MAPK 途径,抑制肿瘤坏死因子表达(TNF↓);消除自由基(GSH↑、GSH-Px↑),保护免疫性肝损伤;抗脂质过氧化(ALT↓、AST↓、MDA↓),保护线粒体膜,促进肝细胞生长[20]~[26],[28],[29]薯蓣皂苷 结肠炎C57BL/6 小鼠 (i.p.25 mg/kg 薯蓣皂苷)、小儿UC 患者结肠LPMCs(200 ng/mL 薯蓣皂苷)山药皮 淡水养殖鲤鱼模型 (质量分数2%的山药皮)低剂量增强IEC 先天免疫力 (AMP↑、β-defensin1↑、βdefensin10↑、RegIIIγ↑);高剂量控制过度的适应性免疫反应,减少促炎因子产生(TNF-α↓、IL-1β↓、IFN-γ↓)和NFκB,减少炎性细胞存活(LPMC↓)调节肠道菌群(拟杆菌↑、黄杆菌↑、乳杆菌↑、肠杆菌↓、希瓦氏菌↓、假单胞菌↓、SCFAs↑);修复肠道防御屏障(CAT↑、SOD↑、IL-1β↓、occludin↑和ZO-1↑、通路因子TLR4-NFκB↑)[27][6]
低剂量薯蓣皂苷治疗可以促进抗菌肽(Antimicrobial peptide,AMP)表达,上调AMP 相关基因如β-防御素(β-defensin)、RegIIIγ,增强肠上皮细胞(Intestinal epithelial cell,IEC)增殖,从而激活免疫;而高剂量薯蓣皂苷可以减少促炎因子和固有层单核细胞(lamina propria mononuclear cells,LPMC)水平,控制过度的适应性免疫反应。总之,薯蓣皂苷可以通过修复肠黏膜屏障,发挥肠道免疫功能[27]。
此外,研究显示饲喂山药皮能够提升肠道酶活性和抗炎水平,增加短链脂肪酸 (Short-chain fatty acids,SCFAs)含量,抑制肠道病原体生长。作为水产养殖饲料添加剂,提升鲤鱼免疫力[6]。
2.2 抗炎
体内炎症反应与阿尔兹海默症(Alzheimer's disease,AD)、炎症性肠病(Inflammatory bowel disease,IBD)、动脉粥样硬化、肥胖等慢性疾病的发生息息相关[29]。如表3所示,山药全粉明显上调碳酸酐酶活性,下调iNOS、COX-2、IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α 等炎症因子水平,对炎症有干预效果[30]。山药皮提取物可以显著降低一氧化氮(Nitric oxide,NO)、粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子(Granulocyte -macrophage colony -stimulating factor,GM-CSF)的表达,促进p65 核位移,并且抑制ROS 产生,通过转录因子NF-E2 相关因子2(Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2,Nrf2)核位移,上调下游抗氧化酶,如血红素加氧酶(Heme oxygenase,HO)-1、腺嘌呤二核苷酸醌氧化还原酶(NADPH quinine oxidoreductase,NQO)-1[31]。
表3 山药抗炎功能研究现状
Table 3 Research status of anti-inflammatory function of Chinese yam

受试物 实验模型 作用效果及机制 参考文献山药全粉 半胱胺诱导的十二指肠溃疡SD 大鼠(i.g.400 mg/kg,2 g/kg CY)COX-2↓、iNOS↓、IL-1β↓、IL-6↓、TNF-α↓,CA IX、XII 和XIV↑[30]山药皮 LPS 诱 导RAW264.7 细 胞,H2O2 诱 导HCT116 结肠上皮细胞 (50,100 μg/mL CY peel),DSS 诱 导 结 肠 炎BALB/c 小鼠(i.g.50,100 mg/kg CY peel)薯蓣皂苷 3T3-11 脂肪细胞和巨噬细胞共培养(10 μmol/L 薯蓣皂苷),LPS 诱导的PD大鼠 (i.p.10 mmol/kg·L 薯蓣皂苷),卵清蛋白致敏BALB/c 小鼠 (i.g.100,200 mg/kg 薯蓣皂苷),棕榈酸酯诱导人脐静脉内皮细胞(0.25,0.5 μg/mL 薯蓣皂苷)降低炎性细胞因子的表达(NO↓、GM-CSF↓、IL-1β↓、IL-6↓、IL-12↑、TNF-α↓、iNOS↓、COX-2↓、p65 核位移↓);抑制氧化应激(ROS↓),通过Nrf2 核位移上调下游抗氧化酶(HO-1↑、NQO-1↑)缓解机体炎症(CK-2↓、JNK↑、NF-κB↑、AP-1↑),减少巨噬细胞产生炎性介质(ROS↓、IL-1↓、IL-6↓);促进脂肪细胞分化,抑制炎症;抑制TLR- NFκB 信号通路;增强肠道T 细胞免疫,消除体内过敏原;阻断IKKβ/IRS-1 通路,调节MAPK/Akt/NFκB 信号通路,缓解动脉粥样硬化病变相关炎症(改善内皮紊乱及胰岛素抵抗)[31][30],[35]~[38]
进一步发现,山药中主要抗炎成分为多酚类物质和皂苷类物质,山药皮中的多酚成分包含没食子酸、阿魏酸等[32]。体外实验结果证明,山药多
酚能够促进神经生长因子 (Nerve growth factor,NGF)表达,抑制NO 水平,主要作用机制为抑制JNK 信号通路[14,33]。紫山药(Dioscorea alata)中的花青素可以降低小鼠体内促炎因子水平,改善氧化应激,提升一系列紧密连接蛋白(Tight junction protein 1,ZO-1)水平,维护屏障完整[16]。薯蓣皂苷的抗炎机制是通过抑制蛋白激酶(Casein kinase,CK)-2,激活JNK、NF-κB,激活子蛋白(Activator protein,AP)-1,抑制巨噬细胞分泌炎性因子,并且可以促进脂肪细胞分化,抑制肥胖诱导的炎症[34];抑制Toll 样受体 (Toll-like receptors,TLR)TLRNFκB 信号通路,缓解帕金森症(Parkinson's Disease,PD)诱导产生的运动障碍及炎症[35];在过敏小鼠体内增强肠道T 细胞免疫,消除体内过敏原,发挥抗炎作用[36];阻断IKKβ/IRS-1 通路,改善内皮紊乱及胰岛素抵抗,通过MAPK/Akt/NFκB 信号通路缓解动脉粥样硬化病变相关炎症[37]。
2.3 改善胃肠屏障
山药具有健脾补虚,治疗肠胃失调,促进消化的功效。如表4所示,山药组分能够有效缓解抗生素诱导的体重降低,增强胃肠蠕动,使宿主代谢表型趋于正常,从而改善肠道失调[4]。另外,还可以预防急性胃溃疡,其机制与氧化应激作用有关[38]。
表4 山药改善胃肠屏障功能研究现状
Table 4 Research status of beneficial gastrointestinal barrier function of Chinese yam

受试物 实验模型 作用效果及机制 参考文献山药全粉 抗生素诱导Wistar 大鼠 (i.g.3.4 g/kg CYW),消炎痛诱导胃溃疡KM 小鼠(i.g.2.5,7.5 g/kg CY)增强胃肠蠕动(SIP↑),肾保护(尿量↓,尿酸再吸收↓);改善肠道失调,保护胃黏膜[4],[38]山药多糖 盐酸林可霉素诱导肠道菌群失调Wistar 大鼠(p.o.合生元胶囊,含CYP 0.04 g,0.02 g,0.01 g/粒),大黄水煎液诱导脾虚KM 小鼠(i.g.10 g/kg CYP)尿囊素 临床治疗胃炎及消化性溃疡患者(p.o.尿囊素铝0.2 g,3 次/d),耐药性近平滑念珠菌(Candida parapsilosis)(尿囊素纳米颗粒),消炎痛诱导胃溃疡Albino Swiss 小鼠(p.o.尿囊素60 mg/kg)调节肝功能相关酶的活性 (总胆红素↑、ALT↑),调节胃肠激素水平(血管活性肠肽↑、胃动素↑、生长抑素↑和P 物质↑),改善胃肠道对水和电解质的运输能力(GE↑、SIP↑);优化肠道菌群结构(梭菌纲↑、芽孢杆菌纲↑、产芽孢杆菌纲↑),调节肠道微生态(双歧杆菌↑、乳酸杆菌↑、大肠杆菌↓、粪肠球菌↓、SCFAs↑);在肠道上皮细胞表面形成亲水凝胶层,维护肠道屏障结构促进黏液合成及分泌,减轻有害物对胃黏膜细胞的损伤,保护胃肠黏膜[40]~[45][43],[45],[46]
CYP 能显著抑制脾虚小鼠胃排空(Gastric emptying,GE)及小肠推进(Small intestinal propulsion,SIP),促进小肠吸收[39]。胃肠激素又称脑肠肽,其水平与肠道蠕动及传输密切相关。将CYP 与双歧杆菌结合制备微生态调节剂,可以改善胃肠道对水和电解质的运输能力,调节脑肠肽水平[40]。CYP 还能够上调有益菌,下调有害菌,改善菌群多样性,增加SCFA 生成[41]。CYP 可以调节脾虚小鼠体内环氧化酶2 (Cyclooxygenase-2,COX-2)、诱导性一氧化氮合酶 (Induced nitric oxide synthase,iNOS)、IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α 的 表达。综上所述,CYP 主要通过增强机体免疫,调节炎症因子水平及相关激素酶活,维护肠道屏障完整性,达到治疗胃溃疡,调节肠道菌群的作用[42]。
临床采用尿囊素铝治疗胃炎及消化性溃疡患者,研究表明,尿囊素具有抗刺激物,消炎抑菌,生肌作用,可用于胃及十二指肠溃疡,能够减轻有害物对胃黏膜细胞的损伤,保护胃肠黏膜[43]。
2.4 调节糖脂代谢
山药具有调节糖脂代谢的功效。山药中抗性淀粉可以减缓餐后血糖效应,其中,黏液蛋白也发挥了降血糖的功效[5]。如表5所示,CYP 能提高己糖激酶(Hexokinase,HK)、琥珀酸脱氢酶(Succinate dehydrogenase,SDH)活性,降低血清总胆固醇(Total cholesterol,TC)、甘油三酯(Triglyceride,TG)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(Low density lipoprotein cholesterol,LDL-C)、丙二醛(Malondialdehyde,MDA)含量,增加高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(High density lipoprotein cholesterol,HDL-C)含量[32,47-48]。除此之外,CYP 显著增加胰岛细胞存活率,促进抗凋亡基因bcl-2 的表达,上调胰岛素受体 (INSR)、胰岛素受体底物(Insulin receptor substrate,IRS)、磷脂酰肌醇3 激酶(Phosphatidylinositol 3kinase,PI3K)水平,改善胰岛素分泌[10,49]。并且协同抗氧化作用,激活超氧化物岐化酶(Superoxide dismutase,SOD)、过氧化氢酶(Catalase,CAT)、GSH-Px,发挥降血糖、血脂的功能[42,50]。
表5 山药调节糖脂代谢功能研究现状
Table 5 Research status of regulating glucose and lipid metabolism function of Chinese yam
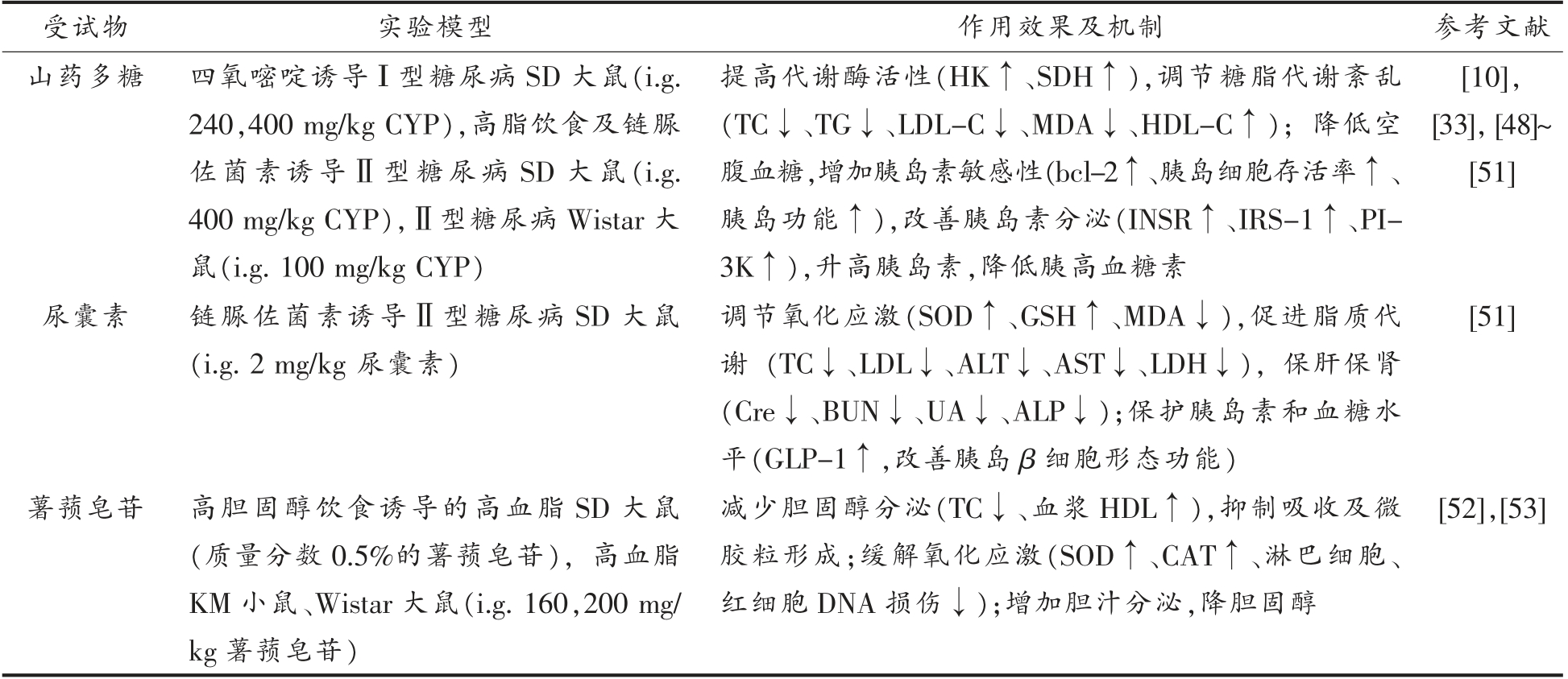
受试物 实验模型 作用效果及机制 参考文献山药多糖 四氧嘧啶诱导Ι 型糖尿病SD 大鼠(i.g.240,400 mg/kg CYP),高脂饮食及链脲佐菌素诱导Ⅱ型糖尿病SD 大鼠(i.g.400 mg/kg CYP),Ⅱ型糖尿病Wistar 大鼠(i.g.100 mg/kg CYP)提高代谢酶活性(HK↑、SDH↑),调节糖脂代谢紊乱(TC↓、TG↓、LDL-C↓、MDA↓、HDL-C↑);降低空腹血糖,增加胰岛素敏感性(bcl-2↑、胰岛细胞存活率↑、胰岛功能↑),改善胰岛素分泌(INSR↑、IRS-1↑、PI-3K↑),升高胰岛素,降低胰高血糖素[10],[33],[48]~[51]尿囊素 链脲佐菌素诱导Ⅱ型糖尿病SD 大鼠(i.g.2 mg/kg 尿囊素)薯蓣皂苷 高胆固醇饮食诱导的高血脂SD 大鼠(质量分数0.5%的薯蓣皂苷),高血脂KM 小鼠、Wistar 大鼠(i.g.160,200 mg/kg 薯蓣皂苷)调节氧化应激(SOD↑、GSH↑、MDA↓),促进脂质代谢 (TC↓、LDL↓、ALT↓、AST↓、LDH↓),保肝保肾(Cre↓、BUN↓、UA↓、ALP↓);保护胰岛素和血糖水平(GLP-1↑,改善胰岛β 细胞形态功能)减少胆固醇分泌(TC↓、血浆HDL↑),抑制吸收及微胶粒形成;缓解氧化应激(SOD↑、CAT↑、淋巴细胞、红细胞DNA 损伤↓);增加胆汁分泌,降胆固醇[51][52],[53]
山药中的尿囊素具有抗氧化作用,能够降低肌酐(Creatinine,Cre)、血尿素氮(Blood urea nitrogen,BUN)、尿酸(Uric acid,UA)、碱性磷酸酶(Alkaline phosphatase,ALP)等肾脏功能相关酶活性,保护肝脏和肾脏。并且改善胰岛β 细胞形态功能,促进胰高血糖素样肽-1 (Glucagon like peptide-1,GLP-1)释放,有效治疗糖尿病[51]。
薯蓣皂苷在动物水平上可以有效缓解高胆固醇饮食诱导的高胆固醇血症。其作用机制为增加胆汁分泌,缓解氧化应激引起的DNA 损伤,降低血浆和肝脏中TC 水平,从而抑制胆固醇吸收[52-53]。
2.5 抗氧化
体内外实验证明,山药具有抗氧化及抗衰老活性。如表6所示,CYP 具有还原性和自由基清除活性,可以下调促凋亡蛋白Bcl-2 相关X 蛋白(Bcl-2 assaciated X protein,Bax)水平[54-55]。此外,CYP 通过调节p53/p21 衰老基因相关通路,抑制神经细胞缺氧性凋亡和大肠杆菌生长[56]。数据显示,CYP 呈剂量依赖型,可调节血清、肝、脑、心、脾等组织的氧化应激,抑制脂质过氧化(Lipid peroxidation,LPO),降低过氧化物酶(Peroxidase,POD)、活性氧(Reactive oxygen species,ROS)和三磷酸腺苷(Adenosine triphosphate,ATP)相关酶的活力水平[57]。抗氧化机制是通过清除自由基,调节系统相关酶活力,抑制衰老基因表达而实现。山药低聚糖也能够清除自由基,实现抗氧化功效[8]。
表6 山药的抗氧化功能研究现状
Table 6 Research status of antioxidation function of Chinese yam

注:CYOs.山药低聚糖。
受试物 实验模型 作用效果及机制 参考文献山药多糖 C57BL/6 小鼠模型 (质量分数1%的薯[55]~[58]蓣皂苷),SD 胎鼠大脑皮层神经细胞(0.05~0.1 g/L CYP),DPPH、ABTS 自由基清除实验,FRAP 法测定总还原力(152.87,168.31,231.82 μg/mL CYP)具有还原性,显著的自由基清除活性 (H2O2↓、DPPH↓、·OH↓、O2-↓),促凋亡/抗凋亡率下调(Bax↓、Bcl-2↑);调节系统抗氧化酶活力(SOD↑、CAT ↑、GSH-Px ↑、LPO ↓、POD ↓、ROS ↓、MDA↓)和ATP 酶活性(Na+/K+-ATP 酶↑、Mg2+-ATP 酶↑、脑系数↑);调节p53/p21 衰老相关通路,抑制神经细胞缺氧性凋亡山药低聚糖 ·OH 自 由 基 清 除 实 验 (100 μg/mL CYOs)自由基清除活性(·OH↓、O2-↓) [8]山药多酚 亚硝酸盐体外清除实验,铁氰化钾还原实验,DPPH 自由基清除实验,脂质过氧化LPO 实验(0.4 g/L 山药多酚)薯蓣皂苷 ISO 诱导的心肌梗塞Wistar 大鼠(p.o.10 mg/kg 薯蓣皂苷)抑制硝酸盐还原酶活性;清除自由基,调节细胞内氧化应激(总多酚还原力↑、烷氧基↓、烷过氧化基↓、DPPH↓),抗脂质过氧化提高抗氧化酶活性(GSH↑、SOD↑、CAT↑、GR↑);缓解红细胞损伤,清除自由基(DPPH↓、·OH↓)[58],[59][60]
山药中含有的多酚类物质具备强还原性,其酚羟基既能与蛋白质结合,又能与金属离子发生螯合作用,并且可以清除体内自由基,抗脂质过氧化,调节胞内氧化应激[58-59]。
薯蓣皂苷对心肌梗塞模型鼠的治疗与其抗氧化作用密切相关,它通过提高GSH、SOD、CAT、GSH-Px、谷胱甘肽还原酶(Glutathione reductase,GR)的活性,减少红细胞和淋巴细胞DNA 损伤,同时清除自由基,缓解氧化应激[60]。
2.6 其它
除上述提到的营养活性以外,山药的功能还集中体现在抗肿瘤免疫[29],改善认知,增肌,促进愈合[61]以及雌激素样作用[62]等方面,研究现状如表7所示。
表7 山药的其它营养功能研究现状
Table 7 Research status of other nutritional functions of Chinese yam

受试物(对应功能) 实验模型 作用效果及机制 参考文献薯蓣皂苷(抗肿瘤免疫)薯蓣皂苷(改善认知、抗老化)尿囊素(雌激素样作用)黑色素瘤C57BL/6 小鼠(i.g.20 mg/kg 薯蓣 皂 苷),AOM/DSS 诱 导 癌 症ICR 小 鼠[p.o.(63.8±1.2)mg/kg 薯蓣皂苷元],结直肠癌HCT-116 和HT-29 细胞系(40 μmol/L 薯蓣皂苷)D-半乳糖诱导的衰老ICR 小鼠(p.o.125 mg/kg 薯 蓣 皂 苷);AD 转 基 因 小 鼠(p.o.80 mg/kg 薯 蓣 皂 苷 元),LPS 诱 导 的C57BL/6 小鼠(p.o.25 mg/kg 薯蓣皂苷),卵 巢 切 除Wistar 大 鼠(p.o.100 mg/kg 薯蓣皂苷),人U251 胶质瘤细胞、RAW264.7 细胞(200 ng/mL 薯蓣皂苷),人角质化细胞(10-6 mol/L 薯蓣皂苷元)KM 小鼠子宫增重实验(i.g.0.02 g/mL 尿囊素),MCF-7 细胞增殖拮抗实验(1 μmol/L 雌激素受体、膜受体GPR30 阻断剂)体内:改变肠道菌群的组成(乳酸菌Lactobacillus↑、萨特氏菌Sutterella↑、拟杆菌Bacteroides↓),提高抗肿瘤免疫活性 (T 细胞浸润↑、IFN-γ↑);体外:调整细胞增殖 (周期素D1),细胞凋亡(p38 MAPK 途径、外源性细胞受体途径、内源性线粒体途径、Akt 途径),迁移和侵袭,氧化反应(HO-1↑、SOD-3↑、caspase-6↑),激活STAT3 通路保护神经(星形胶质细胞激活↓),改善海马5-HT代谢(5-羟基吲哚乙酸↑、L-色氨酸↑、吲哚乙醛↑);增强认知(淀粉样斑块↓、神经原纤维缠结↓、星形胶质细胞↓、Tau 蛋白磷酸化↓),改善神经免疫(IL-2↓)以及更年期认知障碍;改善神经炎症(HMGB-1 / TLR4,TNF-α↓,IL-1β↓,NF-kB↓、MYD88↓);人类皮肤DNA 合成↑、溴脱氧尿苷摄取↑,cAMP↑发挥由ERα 和GPR30 介导的雌激素样作用(E2↑、FSH↑)[62],[63],[69],[70][64],[66],[71],[72][61]尿囊素(改善肌肤,愈合伤口)深度烧伤后愈合患者 (复方肝素钠尿囊素凝胶,早晚涂药)促进组织细胞再生,软化角质层蛋白 [67]
薯蓣皂苷对黑色素瘤细胞、结直肠癌、前列腺癌、乳腺癌、肝癌等多种癌细胞具有细胞毒性[62]。体外通过抑制肿瘤细胞增殖,诱导凋亡及氧化反应,发挥抗肿瘤作用;体内可改变肠道菌群的组成,程序性死亡受体1 (Programmed cell death protein1,PD-1)抗体治疗可增强这一功效,证明山药能提高抗肿瘤免疫活性[63]。
除此之外,薯蓣皂苷能够显著改善衰老引起的认知障碍,增强体内抗氧化酶活力[64]。薯蓣皂苷处理能增强AD 小鼠的认知功能,减少大脑皮层和海马区淀粉状斑块和神经元纤维节,还可以外源激活1,25D3-MARRS/PDIA3/ERp57 通路,触发轴突生长,靶向治疗AD 等神经退行性疾病[65]。抗老化是薯蓣皂苷新开发的功能活性,可以促进人类皮肤DNA 合成,溴脱氧尿苷的摄取,提高细胞内环磷酸腺苷cAMP 水平,说明薯蓣皂苷可以用于老化皮肤上角化细胞增殖修复,且具有安全性[66]。
据报道,山药中的尿囊素可以促进未成熟小鼠子宫指数升高,增加雌二醇(Estradiol,E2)、促卵泡激素(Follicle-stimulating hormone,FSH)等雌性激素水平[61]。临床数据显示,尿囊素可以改善肌肤,促进健康组织细胞再生,软化角质层蛋白,形成弹力的瘢痕表面,对鱼鳞病、手足皲裂等多种皮肤病都有一定改善作用[67-68]。
总结上述文献得出,山药中活性成分能够通过NF-κB、MAPK、AMPK、Akt、p53、Nrf2 等分子靶点,影响下游基因表达,调节细胞因子和氧化还原酶活力,清除自由基及过氧化物,改善血糖水平,发挥免疫、抗炎、调节糖脂代谢、抗氧化等作用。其具体的分子机制如图2所示。

图2 山药营养功能的作用机制
Fig.2 Molecular mechanism of nutritional function of Chinese yam
3 展望
综上所述,山药资源有巨大的经济价值,近年来,国内外对山药营养功能的研究大部分集中于体外水平和动物水平,山药对人体生理的调节机制研究不甚明确[73]。山药成分复杂,其特征组分结构尚不清晰,未来应该进一步明确山药多糖、多酚的结构组成。此外,利用多组学技术阐明山药活性成分对人体保健的作用机制,靶向干预各类慢性疾病,响应“精准营养”的理念,将成为山药营养研究的主要趋势。
目前,新型冠状病毒肺炎(Novel coronavirus pneumonia,NCP)疫情依旧严峻,免疫力低下是易感人群的一大特征,NCP 主要侵犯的器官是肺和脾[74]。通过食疗提升机体免疫力,从而达到预防NCP 的功效,不失为良策。山药作为一种药食同源食材,在中医上常用于治疗脾胃虚弱,食少倦怠、营养不良、虚劳咳嗽等症状[2]。由此可见,将山药开发成新型天然安全的免疫增强剂具有很大的研究价值。
[1]中国科学院中国植物志编辑委员会编.中国植物志[M].第16 卷,北京:科学出版社,1985:60-119.
Editorial Committee of Flora of China,Chinese academy of Sciences.Flora of China[M].Vol.16,Beijing:Science Press,1985:60-119.
[2]LI P,XIAO N,ZENG L,et al.Structural characteristics of a mannoglucan isolated from Chinese yam and its treatment effects against gut microbiota dysbiosis and DSS-induced colitis in mice[J].Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,250(8):116958.
[3]宋君柳.山药品种资源及化学成分研究进展[J].长江蔬菜,2009,6:6-10.
SONG J L.Research progress of yam variety resources and chemical constituents [J].Changjiang Vegetables,2009,6:6-10.
[4]SUN Y,LIU T,SI Y,et al.Integrated metabolomics and 16S rRNA sequencing to investigate the regulation of Chinese yam on antibiotic-induced intestinal dysbiosis in rats [J].Artificial Cells,Nanomedicine and Biotechnology,2019,47(1):3382-3390.
[5]何海玲,单承莺,张卫明.山药研究进展[J].中国野生植物资源,2006,25(6):1-6.
HE H L,SHAN C Y,ZHANG W M.Research progress of Chinese yam [J].China Wild Plant Resources,2006,25(6):1-6.
[6]MENG X,HU W,WU S,et al.Chinese yam peel enhances the immunity of the common carp(Cyprinus carpio L.) by improving the gut defence barrier and modulating the intestinal microflora[J].Fish and Shellfish Immunology,2019,95(10):528-537.
[7]周玥,郭华,周洁.铁棍怀山药中主要营养成分的研究[J].中国食物与营养,2011,17(3):69-71.
ZHOU Y,GUO H,ZHOU J.Study on the main nutrients in Chinese yam[J].Journal of Food and Nutrition in China,2011,17(3):69-71.
[8]CHEN Y F,ZHU Q,WU S.Preparation of oligosaccharides from Chinese yam and their antioxidant activity[J].Food Chemistry,2015,173:1107-1110.
[9]LIU Y,LI H,FAN Y,et al.Antioxidant and antitumor activities of the extracts from Chinese Yam(Dioscoreaopposite Thunb.) flesh and peel and the effective compounds [J].Journal of Food Science,2016,81(6):H1553-H1564.
[10]FAN Y,HE Q,LUO A,et al.Characterization and antihyperglycemic activity of a polysaccharide from Dioscorea opposita Thunb roots [J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2015,16(3):6391-6401.
[11]ZHAO G,KAN J,LI Z,et al.Structural features and immunological activity of a polysaccharide from Dioscorea opposita Thunb roots [J].Carbohydrate Polymers,2005,61(2):125-131.
[12]MA F,WANG D,ZHANG Y,et al.Characterisation of the mucilage polysaccharides from Dioscorea opposita Thunb.with enzymatic hydrolysis[J].Food Chemistry,2018,245:13-21.
[13]李寒冰,刘孟奇,齐向云.怀山药药用 “去皮与否”的合理性研究[J].中成药,2012,34(8):1560-1563.
LI H B,LIU M Q,QI X Y.Study on the rationality of "peeling or not" of Huai Shan medicine[J].Chinese Patent Medicine,2012,34(8):1560-1563.
[14]ROJAS J,BUITRAGO A.Antioxidant activity of phenolic compounds biosynthesized by plants and its relationship with prevention of neurodegenerative diseases[M].Bioactive Compounds:Health Benefits and Potential Applications.Woodhead Publishing,2019:3-31.
[15]初乐,赵岩,和法涛,等.山药多酚的功能及开发应用展望[J].中国果菜,2013(8):45-46.
CHU L,ZHAO Y,HE F T,et al.Function and development and application prospect of polyphenols from yam[J].Chinese Fruit,2013(8):45-46.
[16]CHEN T,HU S,ZHANG H,et al.Anti -inflammatory effects of Dioscorea alata L.anthocyanins in a TNBS-induced colitis model[J].Food and Function,2017,8(2):659-669.
[17]陈运中,陈俊彰.四种山药的药理活性成分比较研究[J].时珍国医国药,2014,25(10):2389-2391.
CHEN Y Z,CHEN J Z.Comparative study on pharmacological active components of four kinds of yam[J].Shizhen Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica,2014,25(10):2389-2391.
[18]YANG D J,LU T J,HWANG L S.Isolation and identification of steroidal saponins in Taiwanese Yam Cultivar (Dioscorea pseudojaponica Yamamoto)[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2003,51(22):6438-6444.
[19]ZHANG X,JIN M,TADESSE N,et al.Dioscorea zingiberensis C.H.Wright:An overview on its traditional use,phytochemistry,pharmacology,clinical applications,quality control,and toxicity[J].Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2018,220(3):283-293.
[20]KONG X F,ZHANG Y Z,WU X,et al.Fermentation characterization of chinese yam polysaccharide and its effects on the gut microbiota of rats[J].International Journal of Microbiology,2009,2009(1687-918X):598152.
[21]赵国华,陈宗道,李志孝,等.山药多糖对荷瘤小鼠免疫功能的影响[J].营养学报,2003,25(1):110-112.
ZHAO G H,CHEN Z D,LI Z X,et al.Effect of yam polysaccharide on immune function of tumorbearing mice[J].Chinese Journal of Nutrition,2003,25(1):110-112.
[22]CHOI E M,HWANG J K.Enhancement of oxidative response and cytokine production by yam mucopolysaccharide in murine peritoneal macrophage[J].Fitoterapia,2002,73(7/8):629-637.
[23]孙雯雯,宋林,李宏峰,等.山药协同替加氟对结肠癌荷瘤裸鼠免疫功能的影响[J].职业与健康,2018,34(8):1043-1045.
SUN W W,SONG L,LI H F,et al.Effects of yam and tegafur on immune function in nude mice with colon cancer tumor[J].Occupational and Health,2018,34(8):1043-1045.
[24]MILLS C D.Anatomy of a discovery:M1 and M2 macrophages[J].Frontiers in Immunology,2015,6(5):1-12.
[25]LIU J Y,YANG F L,LU C P,et al.Polysaccharides from Dioscorea batatas induce tumor necrosis factor-α secretion via Toll-like receptor 4-mediated protein kinase signaling pathways [J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2008,56(21):9892-9898.
[26]LI M,CHEN L X,CHEN S R,et al.Non-starch polysaccharide from Chinese yam activated RAW 264.7 macrophages through the Toll-like receptor 4(TLR4)-NF-κB signaling pathway [J].Journal of Functional Foods,2017,37:491-500.
[27]ZHANG R,GILBERT S,YAO X,et al.Natural compound methyl protodioscin protects against intestinal inflammation through modulation of intestinal immune responses[J].Pharmacology Research and Perspectives,2015,3(2):1-15.
[28]孙延鹏,李露露,刘震坤,等.山药多糖对小鼠免疫性肝损伤的保护作用[J].华西药学杂志,2010,25(1):34-36.
SUN Y P,LI L L,LIU Z K,et al.Protective effect of yam polysaccharide on immune liver injury in mice [J].West China Pharmaceutical Journal,2010,25(1):34-36.
[29]何焱,王继双,张鹏,等.薯蓣皂苷元药理作用及其机制研究进展[J].中草药,2013,44(19):2759-2765.
HE Y,WANG J S,ZHANG P,et al.Research progress of pharmacological action and mechanism of diosgenin[J].Chinese Herbal Medicine,2013,44(19):2759-2765.
[30]PARK J M,KIM Y J,KIM J S,et al.Antiinflammatory and carbonic anhydrase restoring actions of yam powder (Dioscorea spp) contribute to the prevention of cysteamine-induced duodenal ulcer in a rat model[J].Nutrition Research,2013,33(8):677-685.
[31]LIM J S,OH J,BYEON S,et al.Protective effect of Dioscorea batatas peel extract against intestinal inflammation[J].Journal of Medicinal Food,2018,21(12):1204-1217.
[32]杨宏莉,张宏馨,李兰会,等.山药多糖对2 型糖尿病大鼠降糖机理的研究[J].河北农业大学学报,2010,33(3):104-107.
YANG H L,ZHANG H X,LI L H,et al.Study on hypoglycemic mechanism of yam polysaccharide in type 2 diabetic rats[J].Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei,2010,33(3):104-107.
[33]WAN WOO K,WOOK KWON O,YEOU KIM S,et al.Phenolic derivatives from the rhizomes of Dioscorea nipponica and their anti-neuroinflammatory and neuroprotective activities [ J ].Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2014,155(2):1164-1170.
[34]HIRAI S,UEMURA T,MIZOGUCHI N,et al.Diosgenin attenuates inflammatory changes in the interaction between adipocytes and macrophages[J].Molecular Nutrition and Food Research,2010,54(6):797-804.
[35]LI B,XU P,WU S,et al.Diosgenin attenuates lipopolysaccharide -induced Parkinson's disease by inhibiting the TLR/NF-κB pathway[J].Journal of Alzheimer's Disease,2018,64(3):943-955.
[36]HUANG C H,LIU D Z,JAN T R.Diosgenin,a plant-derived sapogenin,enhances regulatory T-Cell immunity in the intestine of mice with food allergy[J].Journal of Natural Products,2010,73(6):1033-1037.
[37]LIU K,ZHAO W,GAO X,et al.Diosgenin ameliorates palmitate-induced endothelial dysfunction and insulin resistance via blocking IKKβ and IRS-1 pathways[J].Atherosclerosis,2012,223(2):350-358.
[38]金佳熹,周冰玉,李柳蓉,等.新鲜山药提取物对小鼠胃溃疡的预防作用研究[J].中国比较医学杂志,2020,30(3):8-13.
JIN J X,ZHOU B Y,LI L R,et al.Study on the preventive effect of fresh yam extract on gastric ulcer in mice[J].Chinese Journal of Comparative Medicine,2020,30(3):8-13.
[39]傅紫琴,蔡宝昌,卞长霞,等.山药及其麸炒品的多糖成分对脾虚小鼠胃肠功能的影响[J].药学与临床研究,2008,16(3):181-183.
FU Z Q,CAI B C,BIAN C X,et al.Effects of polysaccharides from Chinese yam and its bran on gastrointestinal function in mice with spleen deficiency[J].Pharmacy &Clinical Research,2008,16(3):181-183.
[40]李雪欣,于莲,胡孟洋,等.纳米山药多糖结肠靶向微生态调节剂对菌群失调大鼠胃肠激素的影响[J].中国微生态学杂志,2016,28(3):253-255,258.
LI X X,YU L,HU M Y,et al.Effects of colontargeted microecological modulator of nanosyam polysaccharide on gastrointestinal hormones in rats with dysregulated bacterial flora[J].Chinese Journal of Microecology,2016,28(3):253-255,258.
[41]孟德欣,于莲,李雪欣,等.纳米山药多糖合生元结肠靶向微生态调节剂对大鼠肠道菌群的影响[J].中国新药杂志,2016,25(23):2756-2760.
MENG D X,YU L,LI X X,et al.Effect of colon -targeted microecological modulator of nano yam polysaccharide biosensor on intestinal microflora in rats[J].Chinese Journal of New Drugs,2016,25(23):2756-2760.
[42]关倩倩,张文龙,杜方岭,等.山药多糖生物活性及作用机理研究进展[J].中国食物与营养,2018,24(3):11-14.
GUAN Q Q,ZHANG W L,DU F L,et al.Research progress on biological activity and action mechanism of yam polysaccharides[J].Food and Nutrition in China,2018,24(3):11-14.
[43]苏永臣.尿囊素铝对比替普瑞酮治疗胃炎及消化性溃疡的临床应用研究[J].系统医学,2017,2(12):44-46.
SU Y C.Clinical application of allantoin aluminum versus tipredone in the treatment of gastritis and peptic ulcer[J].Systems Medicine,2017,2(12):44-46.
[44]张海燕.山药多糖提取、结构鉴定及对肠道菌群影响的初步研究[D].佳木斯:佳木斯大学,2014.
ZHANG H Y.Preliminary study on extraction,structure identification and effect on intestinal flora of yam polysaccharide[D].Kiamusze:Jiamusi University,2014.
[45]SVETLICHNY G,KÜLKAMP -GUERREIRO I C,DALLA LANA D F,et al.Assessing the performance of copaiba oil and allantoin nanoparticles on multidrug-resistant Candida parapsilosis[J].Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology,2017,40:59-65.
[46]DA SILVA D M,MARTINS J L R,DE OLIVEIRA D R,et al.Effect of allantoin on experimentally induced gastric ulcers:Pathways of gastroprotection[J/OL].European Journal of Pharmacology,2018,821:68-78.
[47]植飞,邢琪昌,汪莹,等.佛手山药多糖对2 型糖尿病大鼠糖脂代谢及氧化应激的影响[J].食品科学,2017,38(5):272-276.
ZHI F,XING Q C,WANG Y,et al.Effects of polysaccharide from Phyllostachyma phyllostachyma on glycolipid metabolism and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetic rats[J].Food Science,2017,38(5):272-276.
[48]金蕊,程银祥,韩凤梅,等.山药多糖对Ⅰ型糖尿病大鼠血糖血脂及肝肾氧化应激的影响[J].湖北大学学报(自然科学版),2016,38(4):298-302.
JIN R,CHENG Y X,HAN F M,et al.Yam polysaccharide on Ⅰdiabetes rats blood lipid and liver and kidney of oxidative stress influence [J].Journal of Hubei University (Natural Science Edition),2016,38(4):298-302.
[49]LI Q,LI W,GAO Q,et al.Hypoglycemic effect of Chinese Yam (Dioscorea opposita rhizoma)polysaccharide in different structure and molecular weight[J].Journal of Food Science,2017,82(10):2487-2494.
[50]董玉香.中医药治疗2 型糖尿病的临床研究进展[J].内蒙古中医药,2016,35(13):148-150.
DONG Y X.Clinical research progress of TCM in the treatment of type 2 diabetes[J].Inner Mongolia Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2016,35(13):148-150.
[51]GO H K,RAHMAN M,KIM G B,et al.Antidiabetic effects of yam (Dioscorea batatas) and its active constituent,allantoin,in a rat model of streptozotocin-induced diabetes[J].Nutrients,2015,7(10):8532-8544.
[52]马海英,赵志涛,王丽娟,等.薯蓣皂苷元和黄山药总皂苷抗高脂血症作用比较[J].中国中药杂志,2002,27(7):528-531.
MA H Y,ZHAO Z T,WANG L J,et al.Comparison of anti -hyperlipidemia effect between diosgenin and total saponins of Huangshan herb[J].China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2002,27(7):528-531.
[53]SON I S,KIM J H,SOHN H Y,et al.Antioxidative and hypolipidemic effects of diosgenin,a steroidal saponin of yam (Dioscorea spp.),on high-cholesterol fed rats[J].Bioscience,Biotechnology and Biochemistry,2007,71(12):3063-3071.
[54]TEMEL R E,BROWN J M,MA Y,et al.Diosgenin stimulation of fecal cholesterol excretion in mice is not NPC1L1 dependent[J].Journal of Lipid Research,2009,50(5):915-923.
[55]YANG W,WANG Y,LI X,et al.Purification and structural characterization of Chinese yam polysaccharide and its activities[J].Carbohydrate Polymers,2015,117:1021-1027.
[56]向勤,胡微煦,蒲明,等.山药多糖对神经细胞毒性及抗缺氧/复氧诱导的神经细胞凋亡的影响[J].中药药理与临床,2013,29(3):94-96.
XIANG Q,HU W X,PU M,et al.Effects of yam polysaccharide on neuronal cytotoxicity and anti -hypoxia/reoxygenation induced neuronal apoptosis[J].Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica,2013,29(3):94-96.
[57]王远辉,余晓宇.铁棍山药多糖纯化及抗氧化活性[J].食品科技,2018,43(3):165-172,180.
WANG Y H,YU X Y.Purification and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Dioscorea timoides[J].Food Science and Technology,2018,43(3):165-172,180.
[58]孟月丽,张庆岭.铁棍山药皮中多酚类化合物体外抗氧化作用研究[J].中医学报,2016,31(5):707-710.
MENG Y L,ZHANG Q L.Study on the antioxidant activity of polyphenols in Chinese yam bark [J].Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2016,31(5):707-710.
[59]涂宝军,马利华,秦卫东,等.超声波辅助提取山药皮多酚工艺及酚类的鉴别研究[J].中国食品添加剂,2014(1):75-81.
TU B J,MA L H,QIN W D,et al.Ultrasonicassisted extraction of polyphenols from Chinese yam bark and identification of phenols[J].Food Additives in China,2014(1):75-81.
[60]SALIMEH A,MOHAMMADI M,RASHIDI B.Preconditioning with diosgenin and treadmill exercise preserves the cardiac toxicity of isoproterenol in rats[J].Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry,2013,69(2):255-265.
[61]DONG M,MENG Z,KUERBAN K,et al.Diosgenin promotes antitumor immunity and PD-1 antibody efficacy against melanoma by regulating intestinal microbiota [J].Cell Death and Disease,2018,9(10):1039.
[62]郑晓珂,张贝贝,曾梦楠,等.尿囊素雌激素样作用[J].药学学报,2018,53(1):68-73.
ZHENG X K,ZHANG B B,ZENG M N,et al.The estrogen-like effect of allantoin[J].Acta Pharmacologica Sinica,2018,53(1):68-73.
[63]CHEUNG K L,KHOR T O,HUANG M T,et al.Differential in vivo mechanism of chemoprevention of tumor formation in azoxymethane/dextran sodium sulfate mice by PEITC and DBM[J].Carcinogenesis,2009,31(5):880-885.
[64]CHIU C S,CHIU Y J,WU L Y,et al.Diosgenin ameliorates cognition deficit and attenuates oxidative damage in senescent mice induced by D-galactose[J].American Journal of Chinese Medicine,2011,39(3):551-563.
[65]CAI B,ZHANG Y,WANG Z,et al.Therapeutic potential of diosgenin and its major derivatives against neurological diseases:Recent advances [J].Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity,2020,2020(1):1-16.
[66]HO Y J,TAI S Y,PAWLAK C R,et al.Behavioral and IL -2 responses to diosgenin in ovariectomized rats[J].Chinese Journal of Physiology,2012,55(2):91-100.
[67]刘利平,张元海,蒋瑞明,等.复方肝素钠尿囊素凝胶与祛疤硅酮凝胶治疗烧伤后瘢痕效果比较[J].中国乡村医药,2017,24(19):16-17.
LIU L P,ZHANG Y H,JIANG R M,et al.Comparison of efficacy of compound heparin sodium allantoin gel and quscar silicone gel in the treatment of post-burn scar[J].Chinese Rural Medicine,2017,24(19):16-17.
[68]葛锐,袁艳.复方肝素钠尿囊素凝胶联合曲安奈德治疗瘢痕疙瘩疗效研究[J].中国美容医学,2019,28(7):5826-5828.
GE R,YUAN Y.Efficacy of compound heparin sodium allantoin gel combined with triamcinolone acetonide in the treatment of keloid [J].Chinese Journal of Aesthetic Medicine,2019,28(7):5826-5828.
[69]MIYOSHI N,NAGASAWA T,MABUCHI R,et al.Chemoprevention of azoxymethane/dextran sodium sulfate -induced mouse colon carcinogenesis by freeze -dried yam Sanyaku and its constituent diosgenin[J].Cancer Prevention Research,2011,4(6):924-934.
[70]CLEMENCE L,BERTRAND L,JEANNE C.Cyclooxygenase-2 and 5-lipoxygenase pathways in diosgenin-induced apoptosis in HT-29 and HCT-116 colon cancer cells[J].International Journal of Oncology,2010,36:1183-1191.
[71]YANG R,CHEN W,LU Y,et al.Dioscin relieves endotoxemia induced acute neuro-inflammation and protect neurogenesis via improving 5-HT metabolism[J].Scientific Reports,2017,7(1):1-13.
[72]TADA Y,KANDA N,HARATAKE A,et al.Novel effects of diosgenin on skin aging[J].Steroids,2009,74(6):504-511.
[73]龚凌霄,池静雯,王静,等.山药中主要功能性成分及其作用机制研究进展[J].食品工业科技,2019,40(16):318-325.
GONG L X,CHI J W,WANG J,et al.Research progress on main functional components and action mechanism of Chinese yam[J].Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(16):318-325.
[74]刘丽香,陈梦霞,黎轶丽,等.新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情下肿瘤患者居家防护和饮食指导[J].现代肿瘤医学,2020,28(7):1234-1236.
LIU L X,CHEN M X,LI Y L,et al.Home protection and dietary guidance for cancer patients under COVID -19 epidemic [J].Modern Oncology Medicine,2020,28(7):1234-1236.