海参(Sea Cucumber,holothurians)是隶属于棘皮动物门(Echinodermata)、海参纲(Holothuroidea)的海洋无脊椎动物[1]。目前,全球发现的海参多达1 700 多种[2],超过70 多种被用来商业开发[3]。其中,亚太地区种类最多,在我国约有140 多种,可食用的约有20种[4]。海参因具有极高的营养和药用价值,在中国古代被称之为“海中人参”,早在公元200 年前便被用以食用[5]。《本草纲目拾遗》中有记载:海参,味甘咸,补肾,益精髓,摄小便,其性温补,足敌人参,故名海参。海参中蛋白质含量高达40.7%~63.6%[2],其中胶原蛋白占总蛋白的70%[6],同时富含多糖和皂苷、钙、镁、铜等微量元素和少量核酸,且脂肪和胆固醇含量低,被列为八珍之首。
海参生活环境复杂,在适应环境的过程中产生了其它生物体内所没有的具有生物活性的次级代谢物[7]。近几十年来,在海参中发现了多种具有重要生物活性的物质,包括海参肽、海参多糖、海参皂苷、脑苷脂、鞘氨醇、酚类物质等[8],具有抗氧化、抗炎、抗癌、抗血栓、抗糖尿病、抗肥胖、抗菌和肝保护等多种生理功能[9]。因生物活性肽具有来源广泛、性能温和、易消化吸收、活性多样和副作用极低等优点,故其提取纯化工艺和生物学功能成为食品领域研究的热点,且低分子质量的肽相比于其它生物活性物质具有更高的活性、稳定性和特异性[10]。海参肽是指海参经蛋白酶水解后分离纯化,得到的以小分子肽段为主,具有多种功能特性的蛋白水解物。其具有良好的溶解度、稳定性、乳化性和低黏度性,不会被消化系统中的蛋白酶和酸碱性物质破坏其结构,能被人体充分吸收和利用[11],因此具有极大的应用潜力。本文围绕海参肽的生物学功能和作用机理进行综述,以期为海参肽相关产品的进一步开发利用提供理论依据。
1 海参肽及其生物活性
海参富含蛋白质,是制备生物活性肽的良好来源。目前已发现的海参肽具有抗氧化、抗疲劳、免疫调节、抗菌、抗肿瘤、血管紧张素转化酶(angiotensin converting enzyme,ACE)抑制活性、延缓衰老、预防和缓解糖尿病、抗炎等多种生物活性[12-16],在功能性食品、医药、护肤品等领域具有广阔的应用前景。部分海参源生物活性肽的种类、组成和活性见表1。海参活性肽目前最常用的制备方法主要为酶解法,制备得到的海参肽主要以2~20 个氨基酸组成的小分子肽段为主,分子质量大部分在2 ku 以下,富含Glu、Gly 和Pro。海参肽特定的生物活性基于其对应的氨基酸组成与序列,例如具有抗氧化活性的海参肽中高比例的疏水性氨基酸可能与其在脂类中具有更高的溶解度有关[21],而影响氨基酸组成与序列的因素主要包括海参的品种、选用酶的种类、酶解部位和酶解条件。因此,厘清海参肽的生物活性与氨基酸序列和特征之间的关系,对进一步研究其作用机制和活性肽的制备具有重要意义。


2 海参肽的作用机制
2.1 抗氧化
生物体内的活性氧(Reactive oxygen species,ROS)主要包括羟自由基、超氧阴离子、过氧化氢和一氧化氮等,具有较强的氧化活性[17]。在人体正常生理代谢过程中,ROS 会在超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)、过氧化氢酶、谷胱甘肽酶和抗坏血酸等的作用下保持动态平衡,不会对人体造成损伤。但如果这个平衡被打破,ROS 在体内大量蓄积,过量的ROS 会引起氧化应激反应并干扰机体的正常生理功能,如蛋白质结构修饰、DNA 损伤、细胞信号异常、增殖反应降低和宿主防御缺陷[18]。
现已有大量研究者从海参蛋白水解产物中提取得到具有抗氧化活性的肽[19-21]。研究表明,通过海参肽的抗氧化作用,可降低氧化应激诱导的细胞毒性、缓解线粒体自噬、提高百草枯诱导后线虫的成活率,肽段中具有抗氧化作用的氨基酸(Cys、Met、Tyr、His、Try 和Phe)能作为还原剂直接参与保护细胞,激活氧化应激相关的蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B,Akt)信号通路[22]。亓新学等[23]研究发现海参小分子肽能通过改善氧化损伤来调节下丘脑-垂体-性腺轴或睾酮-促黄体生成素(luteinizing hormone,LH)反馈机制,达到改善训练导致昆明小鼠血睾酮水平下降的目的[23]。海参肽的抗氧化能力与酶解条件、分子质量、氨基酸的组成序列和多肽结构息息相关[24-27]。多项研究表明低分子质量的海参肽具有更强的抗氧化活性[28]。海参小分子多肽通过促进细胞增殖、降低ROS 和丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)水平、提高抗氧化酶活性,清除1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl,DPPH)和OH·,来减轻氧化损伤[29];Zheng等[30]采用自溶法从海参肠中获得的抗氧化活性寡肽能保护OH·引起的DNA 损伤。此外,海参肽通过和松果肽组装成双肽,不规则卷曲程度增大,暴露出更多活性位点,从而更容易与自由基结合,抗氧化活性增强[31]。海参肽的部分抗氧化作用机制见图1。

图1 海参肽的抗氧化作用机制
Fig.1 Antioxidant mechanism of sea cucumber peptides
2.2 抗衰老
衰老是人体在生长发育成熟之后,受遗传和环境的影响而逐渐发生的不可逆的衰退过程,以生理和心理变化为主[32]。目前关于衰老的主要理论和假说包括自由基理论[33]、线粒体损伤理论[34]、炎症学说[35]等。皮肤的衰老在机体衰老的过程中尤为明显,主要体现在胶原蛋白含量的减少和成纤维细胞增殖率的降低[36-37]。
海参多肽的抗衰老活性主要表现在延长寿命和延缓皮肤衰老。研究表明,海参多肽通过上调Klotho 基因表达、激活SOD 和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(glutathione peroxidase,GSH-Px)活力、抑制脂质过氧化和蛋白氧化延长果蝇的寿命[38];增强线虫的抗氧化防御系统,减少细胞内ROS 积累,清除体外DPPH 自由基,减少年龄色素,延缓生理衰老[12];宋淑亮等[39]研究发现海参肽通过加快NIH/3T3 细胞由G1 期向S 期转变来促进细胞增殖,同时上调I 型胶原蛋白及基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂-1(tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1,TIMP-1)的表达并抑制基质金属蛋白酶-1(matrix metalloproteinase-1,MMP-1)的表达,增加胶原蛋白分泌量,延缓皮肤衰老。海参肽的部分抗衰老作用机制见图2。

图2 海参肽的抗衰老作用机制
Fig.2 Anti-aging mechanism of sea cucumber peptides
2.3 改善学习记忆
学习和记忆是大脑高级神经功能之一,海马、额叶、神经元细胞和神经突触是大脑中与学习记忆相关的主要部分[40]。学习记忆功能衰退是一种由社会压力和衰老所引起的复杂的神经系统发育障碍,是一种严重的亚健康问题,常伴随着学习能力衰退、认知障碍和记忆障碍3 个特征[41],严重的能导致中枢神经系统疾病,如阿尔兹海默症(Alzheimer's disease,AD)和肌萎缩性侧索硬化症[42],AD 发生的典型症状包括胆碱能系统缺陷、氧化应激、炎症反应、海马神经元死亡、神经元纤维缠结和淀粉样斑[43]。
海参肽能分别通过调节胆碱能系统絮乱、修复海马CA1 和CA3 区域神经元细胞、增强尼氏体数、上调磷酸化钙/钙调蛋白依赖性蛋白激酶II(phospho-Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II,p-CaMKII)、磷酸化环磷腺苷反应成分结合蛋白(phosphated cylinc AMP response element binding protein,p-CREB)和脑源性神经营养因子(brain-derived neurotrophic factor,BDNF)的 表达、上调海马中学习记忆相关的长时程增强(longterm potentiation,LTP)通路、提高脑中多不饱和脂肪酸水平、下调脑中组蛋白乙酰转移酶(histone acetyltransferase,HAT)过度活化,使组蛋白乙酰化修饰达到正常的动态可逆水平来改善记忆[44-45];此外分子对接结果显示其主链和AChE 通过疏水键和氢键相互作用来抑制AchE 活性、增强能量代谢、激活蛋白激酶A/脑源性神经营养因子/神经元生长因子(protein kinase A/ brain-derived neurotrophic factor/ nerve growth factor,PKA/BDNF/NGF)信号通路来发挥神经保护作用,缓解和改善记忆障碍[46]。海参肽的部分改善学习记忆作用机制见图3。

图3 海参肽改善学习记忆能力作用机制
Fig.3 Learning and memory improvement mechanism of sea cucumber peptides
注:钙调蛋白(calmodulin,CaM);耗氧率(oxygen consumption rate,OCR)。
2.4 抗疲劳
长期疲劳可能引起与生物调节和免疫系统相关的疾病,例如衰老、抑郁、癌症、多发性硬化症和帕金森病[47]。同时,糖尿病、甲亢、贫血、高体重指数和肝脏疾病也能导致疲劳的发生[48]。疲劳产生的机制极为复杂,通常由能量供应不足、次生代谢物产生、氧化应激反应、炎症和免疫功能障碍等多种因素的共同影响造成[49]。近年来的研究发现能量供应不足和蛋白质代谢中次生代谢产物的积累是疲劳产生的主要原因[50]。
海参肽的抗疲劳作用主要通过提高线粒体功能和减少炎症细胞因子的释放来完成。研究表明海参肽通过提高线粒体的功能,达到维持机体能量平衡、减少代谢物积累、调节糖异生和脂肪分解代谢、提高抗氧化能力来改善小鼠的运动能力,起到抗疲劳作用[51];促进能量代谢相关酶的合成并增加肌肉收缩时的能量补充、激活核因子E2 相关因子2(nuclear factor E2-related factor,NRF2)和腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶/过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ 共激活 因子-1α(AMP-activated protein kinase/peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α,AMPK/PGC-1α)信号通路抑制氧化应激,且分子质量更低、抗疲劳氨基酸残基(例如Leu、Ile 和Val)比例更高的海参肽的抗疲劳功效更优[52]。Ye等[53]的研究发现海参肽能抑制因力竭导致的Toll 样受体4(Toll like receptor 4,TRL4)的过表达和核转录因子κB(nuclear factorκB,NF-κB)信号通路的激活,减少炎症细胞因子的释放来缓解疲劳。此外,海参肽还能通过增加肌组织糖原含量和ATP 生成能力达到抗疲劳功效[54]。海参肽的部分抗疲劳作用机制见图4。
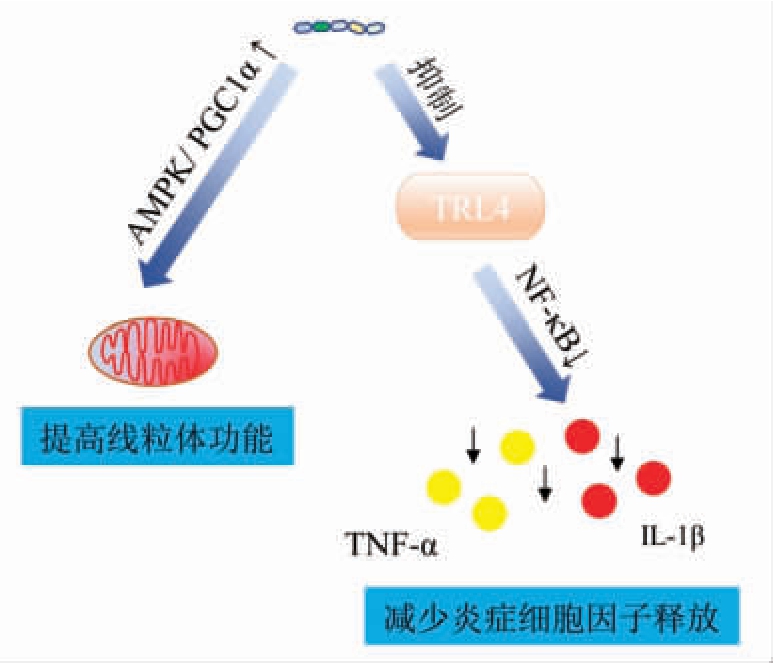
图4 海参肽的抗疲劳作用机制
Fig.4 Anti-fatigue mechanism of sea cucumber peptides
注:过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体(peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha,PPARα);白细胞介素1β(interleukin-1 beta,IL-1β)。
2.5 降血压
高血压现如今已是最常见的慢性疾病之一,世卫组织统计显示全球三分之一的成年人的血压偏高,高血压每年导致全球940 万人死亡[55]。人体内的ACE 是血压调节过程中的关键酶,能将非活性的血管紧张素Ⅰ转化成能高效收缩血管功能的血管紧张素Ⅱ,使舒缓激肽失活,引起血压升高[56]。生物活性肽的降血压作用就是对ACE 活性的抑制作用。从ACE 和其抑制药物的配合物x 射线晶体结构发现氢键和疏水相互作用是影响ACE 稳定性和抑制作用的两种主要相互作用[57]。
研究显示海参肽中的Arg、His 和Asn 残基通过氢键和π 键与ACE 上的活性口袋S2 残基结合,并与Zn2+相互作用,占据ACE 的活性中心,抑制ACE 的活性[58];Forghani等[59]研究发现了3 种具有ACE 抑制活性的海参肽表现出混合抑制模式,且易被ACE 降解,但ACE 抑制活性并没有发生太大变化,说明其混合抑制模式可能是由降解后新生成肽段产生的,而另一种未被ACE 降解的肽则表现出非竞争性抑制模式。此外,通过添加外源Pro 改性修饰后的海参肽与ACE 形成的氢键数量增加,且肽N 端的Pro 通过改变多肽的刚性结构,进一步改变多肽与ACE 的结合位点,具有更高的ACE 抑制活性[60]。
2.6 抗菌抗肿瘤活性
以往关于海参的抗菌抗肿瘤活性研究主要集中在非蛋白活性物质上,近年来,多项研究表明海参肽作为一种重要的生物活性物质,同样具有良好的抗菌抗肿瘤活性。Beauregard等[61]在海参体腔液中发现了抗菌肽,对几种革兰氏阳性菌和革兰氏阴性菌均具有较强的抑制活性,且在pH 值为5时,抑菌活性达到最大。Schillaci等[62]发现海参体腔细胞胞浆中分子质量小于5 ku 的肽对多种革兰氏阳性菌和革兰氏阴性菌具有广谱抑菌活性,可能具有抗菌特性的肽H1 和H2 在质量浓度为12.5 mg/mL 时对大多数革兰氏阳性和革兰氏阴性菌具有广谱抑菌活性,并且在质量浓度为3.1 mg/mL 时能显著抑制葡萄球菌和铜绿假单胞菌生物膜的形成。在此研究基础上,Cusimano等[63]设计出了一种H2 衍生多肽H2d,合成肽H2d 具有更高比例(27%)的疏水性氨基酸残基、更明确的三级结构和两亲性,与细菌膜的相互作用进一步增强,对单增李斯特菌株的抑制作用也比H2 更强。海参肽同时具有良好的抗肿瘤活性,其能通过抑制磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/蛋白激酶B(phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/protein kinase B,PI3K/Akt)信号通路,抑制肿瘤细胞的生长、促进人乳癌MCF-7 细胞的凋亡[64]。Mao等[65]研究则表明海参肽通过调控小非编码RNA——miR-378a-5p 靶向的抑癌基因TUSC2,抑制肿瘤生长,延长肺癌小鼠生存时间。海参肽的抗菌作用机制见图5。
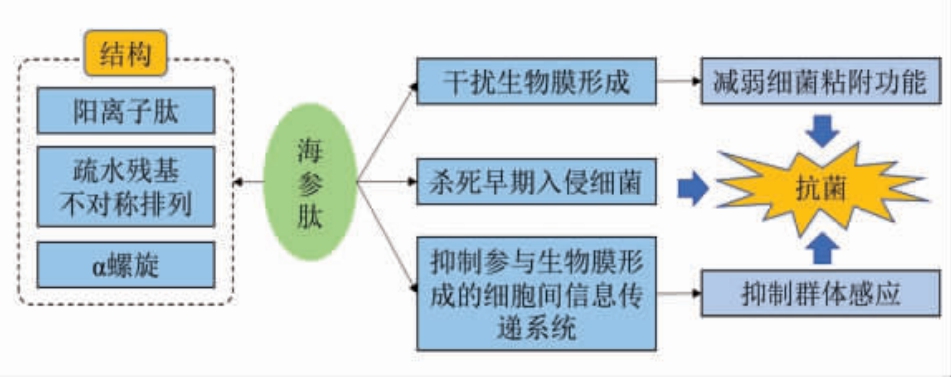
图5 海参肽的抗菌作用机制
Fig.5 Antimicrobial mechanism of sea cucumber peptides
2.7 免疫调节
免疫系统功能分为免疫防御、免疫监视和免疫自稳,在预防和抵御疾病中起着关键作用[66]。宿主对病原体的特定免疫反应又包括细胞免疫和体液免疫[67]。生物活性肽能通过影响体内淋巴细胞增殖,提高抗病毒能力的同时,加强机体免疫力,发挥免疫调节功能[68]。
海参肽主要通过激活CD3ζ 和ζ 链关联蛋白激 酶(zeta chain associated protein kinase 70,ZAP-70)介导的信号通路、上调NF-κB 和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)信号通路,发挥免疫调节作用。海参肽增加了巨噬细胞的吞噬作用和自然杀伤(natural killer,NK)细胞的活性,通过细胞免疫和体液免疫增强适应性免疫应答,刺激辅助性T(T helper,Th)细胞、分泌细胞因子和产生相关抗体,并通过影响T 细胞表面重要分化抗原CD3ζ 和ZAP-70介导的信号通路激活T 淋巴细胞,增强免疫功能[69-70];Nan等[71]研究发现海参肽则能通过上调NF-κB/MAPK 信号通路激活RAW264.7 巨噬细胞,发挥免疫调节作用。
2.8 降血糖
糖尿病是一种复杂的以高血糖为特征的慢性代谢病,全球范围内的患病人数呈爆炸式增长,其中90%以上都为Ⅱ型糖尿病[72]。胰岛素抵抗是Ⅱ型糖尿病发生的主要原因,因其复杂的信号通路和存在如视网膜病变、肾病和心血管疾病等多种并发症,治疗起来极为复杂[73]。
研究发现海参肽能抑制二肽基肽酶IV(dipeptidyl peptidase-IV,DPP-IV)活性,分子对接结果表明了低分子质量的海参肽与DPP-IV 抑制剂阿拉格列汀具有相似的结合模式(与DPP-IV内腔中Glu205、Glu206、Arg125、Phe 357、Arg358、Tyr547、Ser630、Tyr631 和Tyr662 残基紧密结合,抑制其活性),其中分子质量小于3 ku 肽段的DPP-IV 抑制活性最强[75];通过促进前体脂肪细胞3T3-L1 和高胰岛素诱导的胰岛素抵抗型人肝癌细胞HepG2 对葡萄糖的摄取,减轻胰岛素抵抗,促进葡萄糖转运及糖原合成,改善Ⅱ型糖尿病小鼠的血糖调节[74-75];此外,海参肽还能通过提高机体的抗氧化作用和免疫力达到降血糖和防治糖尿病并发症[76]。Li等[77]用海参肽对Ⅱ型糖尿病模型小鼠饮食干预后,利用代谢组学和蛋白质组学对尿液成分进行了分析,结果表明海参肽处理组能显著降低尿葡萄糖和尿素,且不同处理组小鼠的尿蛋白表达均存在差异。
2.9 抗炎
炎症是机体对外界刺激的一种防御反应,机体通过产生自发反应维持自身稳态,但炎症反应同样是多种疾病的发病基础,目前普遍认为慢性低度全身性炎症对代谢性疾病的发生和发展起到了关键作用[78],因此补充具有抗炎作用的药物或生物活性物质,对炎症相关代谢性疾病能起到治疗效果[79]。
海参肽能分别通过抑制TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB和MAPK 信号通路,下调促炎细胞因子转录,上调抗炎因子转录,减轻炎症反应[80];Song等[81]研究发现海参肽还能通过诱导RAW264.7 巨噬细胞血红素氧化酶1(heme oxygenase-1,HO-1)的表达,下调促炎细胞因子转录;Zhang等[82]发现海参肽能阻断白细胞向受损部位迁移,保护CuSO4 诱导的神经肥大损伤,发挥抗炎作用。此外,具有抗炎活性的海参肽中富含Gly、Glu 和Asp,推测其抗炎活性可能与氨基酸的组成、序列和分子质量有关[81]。海参肽的抗炎作用机制见图6。
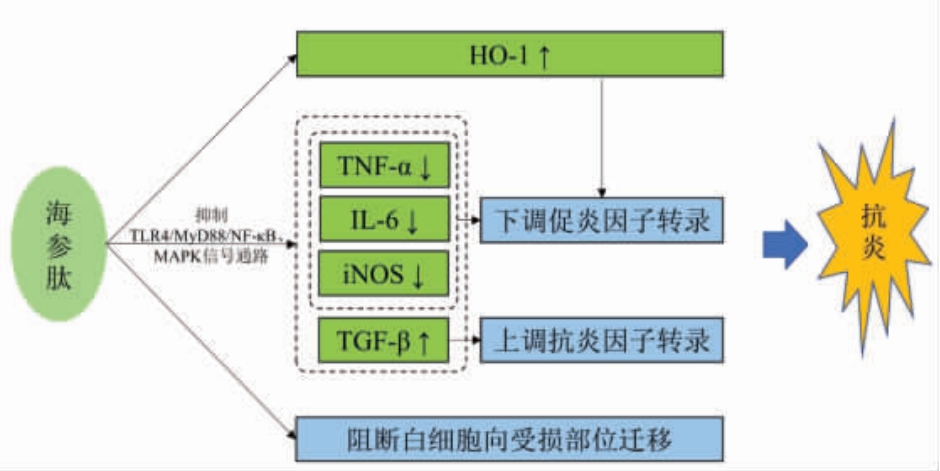
图6 海参肽的抗炎作用机制
Fig.6 Anti-inflammatory mechanism of sea cucumber peptides
注:诱导型一氧化氮合成酶(inducible nitric oxide synthase,iNOS);肿瘤生长因子β(tumor growth factor β,TGF-β)。
2.10 其它活性
海参肽除了抗氧化、抗衰老、改善学习记忆能力、抗疲劳、ACE 抑制、抗菌抗肿瘤、免疫调节、血糖调节和抗炎活性外,还具有金属离子螯合能力、改善创面愈合、促进成骨细胞增殖分化等多种作用,Liu等[83]用碱性蛋白酶酶解海参,分离纯化得到具有锌螯合能力的锌螯合肽ZCP,其锌螯合能力为33.31%,等温滴定量热分析表明一个ZCP 能与两个锌离子的结合,且结合过程是吸热的,红外光谱分析表明多肽通过羧基和酰胺配体和锌离子结合,为锌螯合肽的纯化和表征提供了理论基础。Li等[84]研究发现口服海参小分子寡肽能加速糖尿病小鼠的皮肤创面愈合,机理研究表明海参小分子寡肽通过降低IL-6、IL-8、TNF-α、CC 族趋化因子配体2(CC chemokine ligand 2,CCL2)和C-反应蛋白(C-reactive protein,CRP)水平,提升IL-10水平,降低炎症反应;提高基质细胞衍生因子-1(stromal cell-derived factor-1 alpha,SDF-1α)、NO 和血管内皮生长因子(vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF)的表达,促进血管生成,并在伤口愈合初期增强抗氧化防御体系,改善糖尿病小鼠的创面愈合能力。Yang等[85]研究了海参肽的成骨活性,发现海参肽能促进细胞增殖、分化和矿化,且呈量效关系,作用机理研究表明海参肽可能是通过激活WNT/β-catenin 和骨形态发生蛋白/丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(bone morphogenetic protein/mitogen-activated protein kinase,BMP/MAPK)信号通路实现的,体内试验表明海参肽能显著抑制卵巢切除小鼠血清中NF-κB 受体活化因子配体(receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand,RANKL)、碱性磷酸酶(alkaline phosphatase,ALP)和抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶(tartrate resistant acid phosphatase,TRAP)水平,增加骨钙素和骨保护素水平。Zhang等[86]通过体外和计算机模拟实验发现从海参中分离得到的肽具有抑制ACE、α-淀粉酶和脂肪酶的功效,具有相同序列的肽能够通过调整自身的构象与多种酶的活性位点结合,起到抑制效果。
3 海参肽的应用
基于海参肽的多种生物活性,主要应用领域包括功能性食品、护肤品和药物领域。例如对于某些病后时期的患者,消化吸收功能异常,容易造成营养不良的并发症,而低分子质量的海参肽营养价值高,容易被消化道消化吸收且无抗原性,不会出现过敏反应[87],适合术后病人,尤其是对氨基酸消化吸收存在障碍的人群补充营养,加快身体恢复。海参肽能调节血压,增强人体免疫力,抑制肿瘤细胞生长和转移,可作为降血压、增强提质和抗肿瘤的功能性食品。海参肽还具有抗疲劳活性,可用作易疲劳人群和运动员群体的食品制造中。海参肽的抗氧化和抗衰老活性则可应用于护肤品的开发。
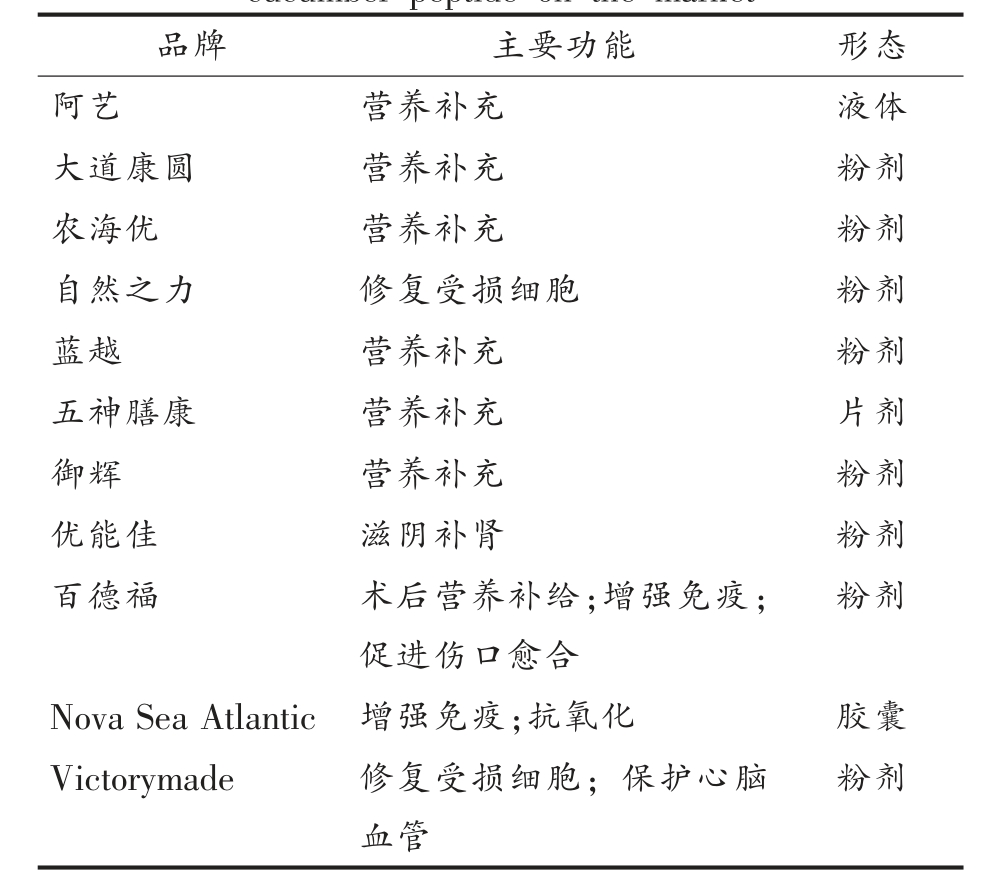
目前,海参作为一种营养、功能食品和治疗药物的潜在用途尚未得到充分开发,市场上产品主要以干海参、即食海参为主,以海参为基础的营养保健品和药物较少,同时大量的海参加工副产物被浪费。目前市场上以海参肽为基础的产品主要作为一种营养补充品售卖,大部分中高端海参肽产品多以其复合功效为宣传手段,对于具有某种特定功效海参肽产品的开发相对不足,产品缺少针对性,表2 为国内外市场上常见的含有海参肽的产品。
表2 目前市场上以海参肽为基础的营养保健品
Table 2 Current functional products based on sea cucumber peptide on the market
4 结论
近年来,海参肽因其生物活性,受到越来越多科研人员的重视。此外,海参肽在我国资源丰富,其良好的溶解度、稳定性、乳化性和易被人体消化吸收的特性,决定了海参肽具有开发成营养、功能食品、护肤品和治疗药物的可能,具有广阔的应用前景和市场价值。但相关研究绝大部分仍处于基础研究阶段,报道的海参肽发挥生物活性的作用机制较为局限,不够全面,构效关系不明确,且缺乏广泛的临床应用,导致其成果转换不足,市场上相关产品种类单一,且加工副产物浪费严重,已有多项研究表明海参加工副产物中分离出的活性肽同样具有多种生物活性,若能将其实现工业化生产,对提高海参自身价值、丰富产品种类、延伸产业链和减少环境污染等,都具有重要的现实意义。
综上,对于海参肽的研究还可以从以下几点出发:1)扩展研究方向,明确海参肽的生物活性与海参的年龄、性别和收获季节等之间的关系;2)利用计算机虚拟酶解和分子对接技术,加快海参活性肽的筛选、鉴定和作用机制研究;3)利用光谱技术、生物医学方法和生物活性导向分析,充分识别和表征生物活性肽的化学结构和生物特性,深入探索总结海参肽的生物活性和其结构之间的规律;4)海参肽发挥其生物活性的作用机制是多途径、多靶点的,要进一步完善海参肽的作用机理研究;5)海参肽潜在的药理作用和使用剂量之间的关系需要使用充分的临床试验得到验证和标准化,以获得最佳的功能和生理效益;6)随着食品加工业和现代装备制造技术的发展,为海参副产物生物活性肽的开发利用提供了良好的条件,加大科研成果转换力度,逐步实现海参资源的高值高质化利用。
[1] GIANASI B L,HAMEL J F,MONTGOMERY E M,et al.Current knowledge on the biology,ecology,and commercial exploitation of the sea cucumber cucumaria frondosa[J].Reviews in Fisheries Science &Aquaculture,2020,29(4):582-653.
[2] PANGESTUTI R,ARIFIN Z.Medicinal and health benefit effects of functional sea cucumbers[J].Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine,2017,8(3):341-351.
[3] PURCELL S W,LOVATELLI A,VASCONCELLOS M,et al.Managing sea cucumber fisheries with an ecosystem approach[R].Rome:FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture,2010.
[4] 朱兰兰,吴晶,周德庆.海参的加工利用与品质评价研究进展[J].农产品加工,2015(24):60-63.ZHU L L,WU J,ZHOU D Q.Research progress of processing and quality evaluation in sea cucumber[J].Farm Products Processing,2015(24):60-63.
[5] YANG H,HAMEL J F,MERCIER A.The sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus:History,biology and aquaculture[M].America:Academic Press,2015.
[6] KHOTIMCHENKO Y.Pharmacological potential of sea cucumbers[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2018,19(5):1342.
[7] PANGESTUTI R,ARIFIN Z.Medicinal and health benefit effects of functional sea cucumbers[J].Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine,2018,8(3):341-351.
[8] TIAN Y Y,HU S W,XU H,et al.Long-chain bases from Cucumaria frondosa inhibit adipogenesis and regulate lipid metabolism in 3T3-L1 adipocytes[J].Food Science and Biotechnology,2016,25(6):1753-1760.
[9] XU C,ZHANG R,WEN Z Y.Bioactive compounds and biological functions of sea cucumbers as potential functional foods[J].Journal of Functional Foods,2018,49:73-84.
[10] LIU N X,WANG Y,YANG M F,et al.New rice-derived short peptide potently alleviated hyperuricemia induced by potassium oxonate in rats[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2019,67(1):220-228.
[11] PEREZ -VEGA J A,OLIVERA -CASTILLO L,GOMEZ-RUIZ J A,et al.Release of multifunctional peptides by gastrointestinal digestion of sea cucumber(Isostichopus badionotus)[J].Journal of Functional Foods,2013,5(2):869-877.
[12] GUO K X,SU L N,WANG Y C,et al.Antioxidant and anti-aging effect of sea cucumber protein hydrolyzate and bioinformatic characterization of its composing peptides[J].Food &Function,2020,11(6):5004-5016.
[13] MAMELONA J,SAINT-LOUIS R,PELLETIER E.Nutritional composition and antioxidant properties of protein hydrolysates prepared from echinoderm byproducts[J].International Journal of Food Science and Technology,2010,45(1):147-154.
[14] 陈娅.海参胶原低聚肽对抗结核药物致大鼠肝损伤的实验研究[D].青岛:青岛大学,2018.CHEN Y.Experimental study on the effect of collagen oligopeptide of sea cucumberon the improvement of drug induced liver injury[D].Qingdao:Qingdao University,2018.
[15] LI Y Y,XU J J,SU X R.Analysis of urine composition in type II diabetic mice after intervention therapy using holothurian polypeptides[J].Frontiers in Chemistry,2017,5:54.
[16] ZHAO Y H,LI B F,DONG S Y,et al.A novel ACE inhibitory peptide isolated from Acaudina molpadioidea hydrolysate[J].Peptides,2009,30(6):1028-1033.
[17] LI R,JIA Z Q,TRUSH M A.Defining ROS in biology and medicine [J].Reactive oxygen species(Apex,N.C.),2016,1(1):9-21.
[18] FINKEL T,HOLBROOK N J.Oxidants,oxidative stress and the biology of ageing[J].Nature,2000,408(6809):239-247.
[19] SAFARI R,YAGHOUBZADEH Z.Antioxidant activity of bioactive peptides extracted from sea cucumber(Holothuria leucospilata)[J].International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics,2020,26(4):2393-2398.
[20] ZHANG J,LIU S W,ZHANG Y,et al.Purification and antioxidant ability of peptide from egg in sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus[J].International Journal of Food Properties,2017,20(2):306-317.
[21] ABEDIN M Z,KARIM A A,LATIFF A A,et al.Biochemical and radical-scavenging properties of sea cucumber(Stichopus vastus)collagen hydrolysates[J].Natural Product Research,2014,28(16):1302-1305.
[22] LU M,MISHRA A,BOSCHETTI C,et al.Sea cucumber-derived peptides alleviate oxidative stress in neuroblastoma cells and improve survival in C.elegans exposed to neurotoxic paraquat[J].Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity,2021,2021:8842926.
[23] 亓新学,郭光明.补充海参小分子肽对运动小鼠血睾酮及睾丸组织氧化应激的影响[J].西昌学院学报(自然科学版),2013,27(2):89-92,4-5.QI X X,GUO G M.Research on the effects of the sea cumumber small peptide on the qxidative stress of the serum testosterone of the exercising mice and testicular tissue MDA[J].Journal of Xichang College(Social Science Edition),2013,27(2):89-92,4-5.
[24] JIN H X,XU H P,LI Y,et al.Preparation and evaluation of peptides with potential antioxidant activity by microwave assisted enzymatic hydrolysis of collagen from sea cucumber Acaudina molpadioides obtained from Zhejiang province in China[J].Marine Drugs,2019,17(3):169.
[25] CHAI T T,LAW Y C,WONG F C,et al.Enzyme-assisted discovery of antioxidant peptides from edible marine invertebrates:a review [J].Marine Drugs,2017,15(2):42.
[26] GHANBARI R,ZAREI M,EBRAHIMPOUR A,et al.Angiotensin-I converting enzyme(ace)inhibitory and anti -oxidant activities of sea cucumber(Actinopyga lecanora)hydrolysates[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2015,16(12):28870-28885.
[27] HERNANDEZ -SAMANO A C,HERNANDEZ -LEDESMA B.Release of antioxidant peptides from the body wall proteins of the sea cucumber Isostichopus fuscus[J].Natural Product Communications,2015,10(8):1427-1430.
[28] PAN S K,YAO D R,ZHOU M Q,et al.Hydroxyl radical scavenging activity of peptide from sea cucumber using enzyme complex isolated from the digestive tract of sea cucumber[J].African Journal of Biotechnology,2014,11(5):1214-1219.
[29] LI Y,LI J,LIN S J,et al.Preparation of antioxidant peptide by microwave -assisted hydrolysis of collagen and its protective effect against H2O2-induced damage of RAW264.7 cells[J].Marine Drugs,2019,17(11):642.
[30] ZHENG J,WU H T,ZHU B W,et al.Identification of antioxidative oligopeptides derived from autolysis hydrolysates of sea cucumber(Stichopus japonicus)guts [J].European Food Research and Technology,2012,234(5):895-904.
[31] MA C,SUN N,ZHANG S M,et al.A new dualpeptide strategy for enhancing antioxidant activity and exploring the enhancement mechanism[J].Food&Function,2019,10(11):7533-7543.
[32] SERRANO F,KLANN E.Reactive oxygen species and synaptic plasticity in the aging hippocampus[J].Ageing Research Reviews,2004,3(4):431-443.
[33] HARMAN D.Origin and evolution of the free radical theory of aging:a brief personal history [J].Biogerontology,2009,10(6):783-783.
[34] VASILEIOU P V S,EVANGELOU K,VLASIS K,et al.Mitochondrial homeostasis and cellular senescence[J].Cells,2019,8(7):686.
[35] CEVENINI E,MONTI D,FRANCESCHI C.Inflamm-ageing[J].Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition &Metabolic Care,2013,16(1):14-20.
[36] 王欢.刺参多肽影响NIH/3T3 细胞增殖及Ⅰ型胶原蛋白表达的研究[D].济南:山东大学,2015.WANG H.The preliminary studies of the polypeptide from Stichopus japonicus on the proliferation and type I collagen expression of NIH/3T3 cells[D].Jinan:Shandong University,2015.
[37] 杨坤.叶瓜参提取物的酶法制备及其抗衰老活性研究[D].广州:华南理工大学,2018.YANG K.Study on the enzymatic preparation and anti-aging activities of Cucumaria frondosa Extracts[D].Guangzhou:South China University of Technology,2018.
[38] LIN L Z,ZHU Q Y,ZHENG L,et al.Preparation of sea cucumber(Stichopus variegates)peptide fraction with desired organoleptic property and its antiaging activity in fruit flies and D-galactose-induced aging mice[J].Journal of Functional Foods,2020,69:103954.
[39] 宋淑亮,王欢,梁浩,等.海参肽的分离纯化及其对NIH/3T3 细胞胶原蛋白分泌的影响[J].现代食品科技,2017,33(3):7.SONG S L,WANG H,LIANG H,et al.Isolation and purification of sea cucumber peptide and its impacts on the secretion of collagen by NIH/3T3 cells[J].Modern Food Science &Technology,2017,33(3):7.
[40] LAVENEX P,LAVENEX P B.Building hippocampal circuits to learn and remember:Insights into the development of human memory[J].Behavioural Brain Research,2013,254:8-21.
[41] WU D,ZHANG S Y,SUN N,et al.Neuroprotective function of a novel hexapeptide QMDDQ from shrimp via activation of PKA/CREB/BNDF signaling pathway and its structure -activity relationship [J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2020,68(24):6759-6769.
[42] JOSEPH R.Environmental influences on neural plasticity,the limbic system,emotional development and attachment:a review[J].Child Psychiatry &Human Development,1999,29(3):189-208.
[43] WANG S G,SU G W,ZHANG X,et al.Characterization and exploration of potential neuroprotective peptides in walnut(Juglans regia)protein hydrolysate against cholinergic system damage and oxidative stress in scopolamine-induced cognitive and memory impairment mice and zebrafish[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2021,69(9):2773-2783.
[44] LIN S Y,LU Z Q,XU X M,et al.Sea cucumber peptides attenuated the scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice and rats and the underlying mechanism [J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2022,70(1):157-170.
[45] XU X M,LIANG R,LI D M,et al.Evaluation of sea cucumber peptides-assisted memory activity and acetylation modification in hippocampus of test mice based on scopolamine-induced experimental animal model of memory disorder[J].Journal of Functional Foods,2020,68:103909.
[46] ZHAO Y,DONG Y F,GE Q N,et al.Europrotective effects of NDEELNK from sea cucumber ovum against scopolamine-induced PC12 cell damage through enhancing energy metabolism and upregulation of the PKA/BDNF/NGF signaling pathway [J].Food &Function,2021,12(17):7676-7687.
[47] HSIAO C Y,HSU Y J,TUNG Y T,et al.Effects of Antrodia camphorata and Panax ginseng supplementation on anti-fatigue properties in mice[J].Journal of Veterinary Medical Science,2017,80(2):284-291.
[48] YOU L J,ZHAO M M,REGENSTEIN J M,et al.In vitro antioxidant activity and in vivo anti-fatigue effect of loach(Misgurnus anguillicaudatus)peptides prepared by papain digestion[J].Food Chemistry,2011,124(1):188-194.
[49] LUO C H,XU X R,WEI X C,et al.Natural medicines for the treatment of fatigue:Bioactive components,pharmacology,and mechanisms[J].Pharmacological Research,2019,148:104409.
[50] SURHIO M M,WANG Y,FANG S,et al.Antifatigue activity of a Lachnum polysaccharide and its carboxymethylated derivative in mice[J].Bioorganic &Medicinal Chemistry Letters,2017,27(20):4777-4780.
[51] YU Y H,WU G Q,JIANG Y G,et al.Sea cucumber peptides improved the mitochondrial capacity of mice:A potential mechanism to enhance gluconeogenesis and fat catabolism during exercise for improved antifatigue property[J].Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity,2020,2020:1-17.
[52] WANG Q Q,SHI J Y,ZHONG H,et al.Highdegree hydrolysis sea cucumber peptides improve exercise performance and exert antifatigue effect via activating the NRF2 and AMPK signaling pathways in mice[J].Journal of Functional Foods,2021,86:104677.
[53] YE J,SHEN C H,HUANG Y Y,et al.Anti-fatigue activity of sea cucumber peptides prepared from Stichopus japonicus in an endurance swimming rat model[J].Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2017,97(13):4548-4556.
[54] 余毅豪.海参肽抗疲劳的作用及机制研究[D].无锡:江南大学,2021.YU Y H.Research on anti-fatigue effect and mechanism of sea cucumber peptide[D].Wuxi:Jiangnan University,2021.
[55] World Health Organization.A global brief on hypertension:Silent killer,global public health crisis:World Health Day 2013[R].Geneva:WHO,2013.
[56] ONDETTI M A,RUBIN B,CUSHMAN D W.Design of specific inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme:new class of orally active antihypertensive agents[J].Science,1977,196(4288):441-444.
[57] PINA A S,ROQUE A C A.Studies on the molecular recognition between bioactive peptides and angiotensin-converting enzyme[J].Journal of Molecular Recognition,2010,22(2):162-168.
[58] ZHONG C,SUN L C,YAN L J,et al.Production,optimisation and characterisation of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from sea cucumber(Stichopus japonicus)gonad[J].Food &Function,2018,9(1):594-603.
[59] FORGHANI B,ZAREI M,EBRAHIMPOUR A,et al.Purification and characterization of angiotensin converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides derived from Stichopus horrens:Stability study against the ACE and inhibition kinetics [J].Journal of Functional Foods,2016,20:276-290.
[60] LI J P,LIU Z Y,ZHAO Y H,et al.Novel natural angiotensin converting enzyme(ACE)-inhibitory peptides derived from sea cucumber-modified hydrolysates by adding exogenous proline and a study of their structure-activity relationship[J].Marine Drugs,2018,16(8):271.
[61] BEAUREGARD K A,TRUONG N T,ZHANG H Y,et al.The detection and isolation of a novel antimicrobial peptide from the echinoderm,Cucumaria frondosa.[J].Phylogenetic Perspectives on the Vertebrate Immune System,2001,484:55-62.
[62] SCHILLACI D,CUSIMANO M G,CUNSOLO V,et al.Immune mediators of sea-cucumber Holothuria tubulosa(Echinodermata)as source of novel antimicrobial and anti -staphylococcal biofilm agents [J].Amb Express,2013,3(1):35.
[63] CUSIMANO M G,SPINELLO A,BARONE G,et al.A synthetic derivative of antimicrobial peptide holothuroidin 2 from mediterranean sea cucumber(Holothuria tubulosa)in the control of Listeria monocytogenes[J].Marine Drugs,2019,17(3):159.
[64] WEI W,FAN X M,JIA S H,et al.Sea cucumber intestinal peptide induces the apoptosis of MCF-7 cells by inhibiting PI3K/AKT pathway[J].Frontiers in Nutrition,2021,8:763692.
[65] MAO J,ZHANG Z C,CHEN Y D,et al.Sea cucumber peptides inhibit the malignancy of NSCLC by regulating miR-378a-5p targeted TUSC2[J].Food&Function,2021,12(24):12362-12371.
[66] WOLF A J,UNDERHILL D M.Peptidoglycan recognition by the innate immune system[J].Nature Reviews Immunology,2018,18(4):243-254.
[67] FENG H B,DU X G,TANG J,et al.Enhancement of the immune responses to foot-and-mouth disease vaccination in mice by oral administration of a novel polysaccharide from the roots of Radix Cyathulae officinalis Kuan(RC)[J].Cellular Immunology,2013,281(2):111-121.
[68] 倪明龙,黄海潮.海参肽的生物活性及其应用研究进展[J].轻工科技,2020,36(8):16-17,20.NI M L,HUANG H C.Research progress in the biological functions and application of sea cucumber peptide[J].Light Industry Science and Technology,2020,36(8):16-17,20.
[69] HE L X,ZHANG Z F,SUN B,et al.Sea cucumber(Codonopsis pilosula)oligopeptides:immunomodulatory effects based on stimulating Th cells,cytokine secretion and antibody production[J].Food &Function,2016,7(2):1208-1216.
[70] DU X G,LIAN F L,LI Y K,et al.Peptides from Colochirus robustus enhance immune function via activating CD3ζ-and ZAP-70-mediated signaling in C57BL/6 mice[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2017,18(10):2110.
[71] NAN C,LUO W Q,YAO L J,et al.Activation of murine RAW264.7 macrophages by oligopeptides from sea cucumber(Apostichopus japonicus)and its molecular mechanisms[J].Journal of Functional Foods,2020,75:104229.
[72] WHITING D R,GUARIGUATA L,WEIL C,et al.IDF Diabetes Atlas:Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2011 and 2030[J].Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice,2011,94(3):311-321.
[73] DING M,BHUPATHIRAJU S N,CHEN M,et al.Caffeinated and decaffeinated coffee consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes:A systematic review and a dose-response meta-analysis[J].Diabetes Care,2014,37(2):569-586.
[74] GONG P X,WANG B K,WU Y C,et al.Release of antidiabetic peptides from Stichopus japonicas by simulated gastrointestinal digestion[J].Food Chemistry,2020,315:126273.
[75] 王婷婷.海参肽对Ⅱ型糖尿病大鼠血糖活性调节作用及其机制研究[D].南宁:广西大学,2021.WANG T T.Hypoglycemic effects of peptides from on sea cucumber(Holothuria Nobilis)on typeⅡdiabetic rats and the related mechanisms[D].Nanning:Guangxi University,2021.
[76] 王祖哲,马普,左爱华,等.刺参低聚肽对糖尿病小鼠降血糖作用的研究[J].食品研究与开发,2019,40(8):85-90.WANG Z Z,MA P,ZUO A H,et al.Hypoglycemic effect of Apostichopus japonicus oligo-peptides in alloxan-induced diabetic mice[J].Food Research and Development,2019,40(8):85-90.
[77] LI Y Y,XU J J,SU X R.Analysis of urine composition in type II diabetic mice after intervention therapy using holothurian polypeptides[J].Frontiers in Chemistry,2017,5:54.
[78] BAKER R G,HAYDEN M S,GHOSH S.NF-κB,in flammation,and metabolic disease[J].Cell Metabolism,2011,13(1):11-22.
[79] ESSER N,PAQUOT N,SCHEEN A J.Inflammatory markers and cardiometabolic diseases [J].Acta Clinica Belgica,2015,70(3):193-199.
[80] WAN H T,HAN J J,TANG S S,et al.Comparisons of protective effects between two sea cucumber hydrolysates against diet induced hyperuricemia and renal inflammation in mice[J].Food &Function,2019,11(1):1074-1086.
[81] SONG J J,LI T E,CHENG X,et al.Sea cucumber peptides exert anti-inflammatory activity through suppressing NF-kappa B and MAPK and inducing HO-1 in RAW264.7 macrophages[J].Food &Function,2016,7(6):2773-2779.
[82] ZHANG X M,LI H N,WANG L Z,et al.Antiinflammatory peptides and metabolomics -driven biomarkers discovery from sea cucumber protein hydrolysates[J].Journal of Food Science,2021,86(8):3540-3549.
[83] LIU X Y,WANG Z X,ZHANG J,et al.Isolation and identification of zinc-chelating peptides from sea cucumber(Stichopus japonicus)protein hydrolysate[J].Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2019,99(14):6400-6407.
[84] LI D,LIN L,XU T,et al.Effect of low molecular weight oligopeptides isolated from sea cucumber on diabetic wound healing in db/db mice[J].Marine Drugs,2018,16(1):16.
[85] YANG M L,XU Z,WU D,et al.Characterizations and the mechanism underlying osteogenic activity of peptides from enzymatic hydrolysates of Stichopus japonicus[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2021,69(51):15611-15623.
[86] ZHANG Y,HE S D,RUI X,et al.Interactions of C.frondosa-derived inhibitory peptides against angiotensin I-converting enzyme(ACE),α-amylase and lipase[J].Food Chemistry,2021,367:130695.
[87] 赵兴坤.海参肽的功能特性及其应用[J].中国食品与营养,2003,9(12):31-33.ZHAO X K.Functional properties and application of sea cucumber peptide[J].Food and Nutrition in China,2003,9(12):31-33.