天然产物来源β-葡聚糖具有良好的生理活性,包括抗氧化、抗肿瘤、抗炎,调节血糖以及调节免疫等[1-3]。有文献报道,β-葡聚糖的活性与其结构有着紧密联系,如低分子量的β-葡聚糖具有良好的抗氧化和免疫活性[4-5],高分子、高黏性β-葡聚糖在降胆固醇、血糖调节方面发挥重要作用[6-7]。通过一定手段降解β-葡聚糖或引入其它取代基团来改变其结构也会引起活性的改变[8-9]。科学认识β-葡聚糖结构特征,对于其生理活性研究与应用具有重要意义。
长裙竹荪是一种名贵的食用菌,多糖是其重要营养成分[10]。长裙竹荪含有丰富的水溶性β-1,3-葡聚糖[11]。也有文献报道长裙竹荪多糖中还含有甘露糖、半乳糖以及少量的鼠李糖和葡萄糖醛酸[12-13]。此外,有研究发现,长裙竹荪中葡萄糖的残基类型既有β 构型,也有α 构型[14]。这些研究结果的差异性,导致人们对长裙竹荪多糖的结构产生困扰。本文从长裙竹荪中提取β-葡聚糖,分析其化学组成、结构特征和溶液性质,以期为其活性研究,以及后续相关功能性食品的开发提供参考。
1 材料与方法
1.1 原料与试剂
长裙竹荪,贵州省赤水市。葡萄糖、半乳糖、阿拉伯糖、鼠李糖、半乳糖醛酸、葡聚糖标准品(Mw 2.0×106 u 和2.5×104 u)、碘甲烷,美国Merck(Sigma-Aldrich)公司;葡萄糖醛酸标准品、葡聚糖标准品 (Mw 7.0×104,6.0×104,5.0×104,4.0×104 u 和1.0×104 u)、考马斯亮蓝G-250、牛血清蛋白、没食子酸、耐高温α 淀粉酶、木瓜蛋白酶,上海阿拉丁试剂有限公司;木糖、甘露糖标准品,百灵威科技有限公司;葡聚糖标准品(Mw 5.0×105 u),北京欣经科生物技术有限公司;浓硫酸,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;乙醇、乙酸、磷酸、甲醇、二甲基亚砜等,均为国产分析纯试剂。
1.2 试验仪器与设备
Dionex ICS 5000 离子色谱仪、Nicolet 5700红外光谱仪、Varioskan Flash 多功能酶标仪,美国Thermo Scientific 公司;JSM-7610F 场发射扫描电镜带能谱仪,日本JEOL 公司;ARES-G2 流变仪,美国TA 公司;HPSEC-MALLS 色谱系统,美国WYATT 公司;E2695 液相系统,美国WATERS 公司;GC-MS7890/7000 QQQ,美国Agilent 科技有限公司;AL104 电子天平,上海梅特勒-托利多仪器公司;Rotavapor R-220 SE 旋转蒸发仪,瑞士Buchi 公司;Milli-Q 超纯水仪,美国Millipore 公司;12 L 立式冷冻干燥机,美国LABCONCO 公司。
1.3 长裙竹荪多糖的制备与纯化
1) 原料前处理 将长裙竹荪样品粉碎,以1∶8 的料液比于体积分数为75%乙醇中浸泡24 h,离心除去上清液,加入体积分数为75%乙醇再次浸泡24 h,收集沉淀,烘干,获得竹荪粉末。
2) 多糖制备 将上述乙醇浸泡后的长裙竹荪粉末,按照料液比1∶31 加入蒸馏水,75 ℃提取两次,每次3.5 h,离心(4 800 r/min,10 min),收集上清液,减压真空浓缩,再缓慢加入体积分数为95%乙醇至体系乙醇体积分数达80%,于4 ℃冰箱醇沉过夜。离心(4 800 r/min,5 min),沉淀加水复溶,旋蒸除去乙醇。采用Sevag 法脱蛋白3 次,离心(4 800 r/min,10 min),收集上清液。旋蒸浓缩除去残留的有机试剂,蒸馏水透析3 d(透析袋截留分子质量8 000~14 000 u),将透析液浓缩冻干,得到长裙竹荪多糖 (D.indusiata polysaccharide,DIP)。
3) 多糖纯化 配制质量浓度为1 mg/mL 的竹荪多糖溶液,加入体积分数为0.05%耐高温α-淀粉酶,然后,溶液在98 ℃下酶解30 min,冷却至室温后加入0.025%木瓜蛋白酶,于60 ℃酶解30 min。酶解结束后将溶液温度上升至100 ℃保持15 min 使酶失活。待溶液冷却,缓慢加入无水乙醇,不断搅拌至乙醇体积分数达20%,4.0 ℃静置12 h 过夜。离心(10 000 r/min,15 min)后沉淀加水复溶,旋蒸除乙醇,在4.0 ℃冰箱透析(透析袋截留分子质量8 000~14 000 u)2 d 后冻干。冻干后的多糖加水复溶(1.0 mg/mL),二次醇沉、透析、冻干后得到长裙竹荪纯化多糖 (D.indusiata purified polysaccharide,DIPP)。
1.4 化学组成测定
以葡萄糖为标准品,苯酚硫酸法测定中性糖含量[15]。以牛血清蛋白为标准品,考马斯亮蓝法测定蛋白质含量[16]。采用AOAC 法996.11,用Megazyme 淀粉总量检测试剂盒测定淀粉含量。
1.5 单糖组成测定
取5 mg 多糖样品于厚壁管,在冰浴条件下向其中加入0.5 mL 12 mol/L 浓硫酸搅拌5 min,继续加入2.5 mL 蒸馏水,在100 ℃下油浴2 h 后移入50 mL 容量瓶中蒸馏水定容,稀释5 倍后过0.22 μm 水系滤膜,使用Dionex ICS 5000 离子色谱仪检测其单糖组成[17]。
色谱条件:色谱柱:CarboPacTM PA20 分析柱 (3 mm×150 mm,Dionex,CA)、CarboPacTM PA20保护柱(3 mm×30 mm,Dionex,CA),柱温30.0 ℃。
1.6 傅里叶红外光谱测定
取多糖样品真空干燥,在干燥环境中与溴化钾粉末混合,研磨均匀,压片后采用傅里叶红外光谱仪在400~4 000 cm-1 范围扫描采集红外光谱信号。
1.7 高效尺寸排阻色谱串联多角度激光散射仪(HPSEC-MALLS)分析
多糖用流动相配成1.0 mg/mL 多糖溶液,过3遍0.22 μm 滤膜,得到待测样品,采用HPSECMALLS 分析。仪器色谱系统配有E2695 分离单元,MALLS 多检测器联用系统(美国Wyatt)配有十八角度激光光散射检测器 (LS)、黏度检测器(DP)和示差检测器(RI)。
色谱条件:色谱柱:OHpak SB-G 保护柱(50 mm × 6.0 mm I.D.,10 μm)、OHpak SB-806 HQ(300 mm×8.0 mm I.D.,13 μm)和OHpak SB-804 HQ (300 mm×8.0 mm I.D.,10 μm)(日本Shodex Denko 公司)。流动相:0.1 mol/L NaNO3 溶液(含0.035% proclin 300)
1.8 甲基化与GC-MS 测定
参考Wang 等[18]的甲基化方法,使用GC-MS 7890/7000 QQQ 检测。
选用SPTM-2330 ms 毛细管柱 (30 m×0.25 mm×0.2 μm,美国Merck Supelco)分析。其它条件:进样口温度250 ℃,不分流;升温程序:以2 ℃/min 速度,从160 ℃升至210 ℃,再5 ℃/min 升温至240 ℃,保持20 min;离子化模式:EI(70 kV);MS 扫描范围:m/z 35~400。
1.9 扫描电镜测定
取多糖样品配成1 mg/mL 的多糖溶液,干燥后置铜台上喷金处理,使用JSM-6701F 冷场发射扫描电镜观察表面形貌特征。
1.10 流变性质测定
取多糖样品用蒸馏水溶解,配成质量分数分别为0.1%,0.5%,1.0%,1.5%和2.0%的多糖溶液,使用ARES-G2 流变仪测定表观黏度。在线性黏弹区内选取5%应变作为动态频率测量的应变值,在Oscillatory Frequency 模式下测定多糖溶液黏弹性。
1.11 数据分析
数据采用SPSS 软件进行t 检验,P<0.05 为差异具有统计学意义。
2 结果与分析
2.1 理化性质
从长裙竹荪中提取的水溶性粗多糖得率为5.6%,纯化后得到的组分得率较低,仅1.4%。纯化后,长裙竹荪多糖DIPP 的纯度(中性糖与单糖组成中Glc 的含量)得到很大提升,蛋白质和淀粉含量显著下降。DIP 中的主要组分为Glc,还含有少量的Gal、Man 和GlcA,纯化得到的DIPP 中仅检测到Glc,表明DIPP 是一种葡聚糖。长裙竹荪多糖的单糖组成以葡萄糖为主,通过酶解醇沉的方法可以得到一种纯度较高的非淀粉葡聚糖。
表1 DIP 和DIPP 得率和基本成分分析(n=3,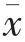 ±s)
±s)
Table 1 Yield and chemical composition of DIP and DIPP(n=3,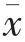 ±s)
±s)

注:-:未检测到;A:得率(%)=多糖质量/干燥子实体质量×100;B:每个值为平均值±标准差,同一列不同小写字母间具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。
?
2.2 红外光谱分析结果
图1是DIPP 的红外光谱图,位于3 394 cm-1和2 924 cm-1 附近的吸收峰分别是由O-H 的伸缩振动和C-H 的伸缩振动引起的[19-20],这是多糖的特征吸收峰。1 633 cm-1 处为结合水引起的吸收峰[21]。1 430~1 200 cm-1 范围的吸收峰是由O-H 变角振动和C-O 的伸缩振动引起的。1 076 cm-1 处的吸收峰是吡喃环的伸缩振动引起的[22],896 cm-1处的吸收峰表明DIPP 的糖苷键存在β 构型[23]。上述结果表明,DIPP 是具有β 构型的吡喃糖。
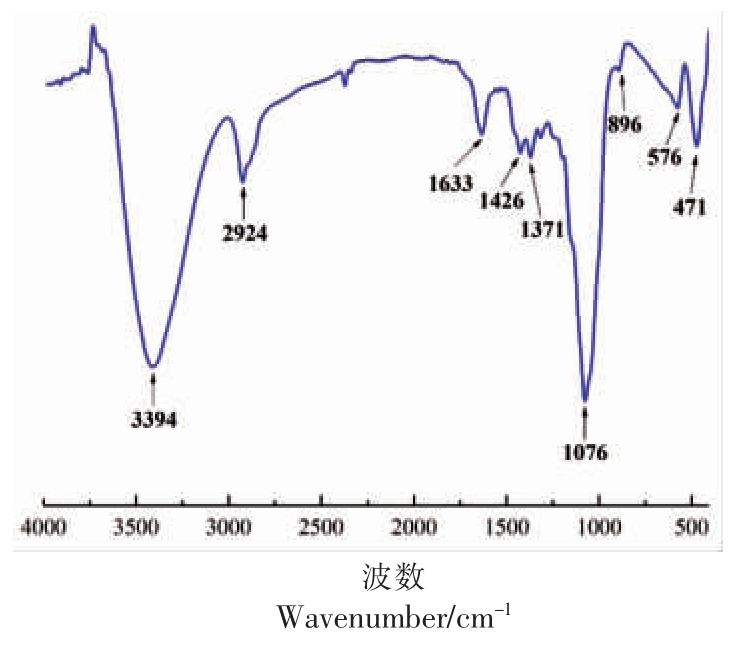
图1 DIPP 的红外光谱图
Fig.1 FT-IR spectrum of DIPP
2.3 HPSEC-MALLS 分析结果
HPSEC-MALLS 是一种简单、有效的分析分子量和链构象参数的技术[24]。图2表明DIPP 是单一组分多糖,表2中DIPP 的回收率为43.5%,这可能是因为DIPP 分子量大、黏度高,导致样品过滤时很多组分被截留。DIPP 的重均分子质量为2.8×106 u,分子质量分布较窄(Mw/Mn=1.5)。在水溶液中,DIPP 特性黏度为1 094.3 mL/g,比已报道的红托竹荪多糖特性黏度([η]=1 350.0 mL/g)要小[18],而高于棘托竹荪多糖([η]=10.9 mL/g)[25]。综上可知,DIPP 是一种均一性良好的水溶性多糖,具有一定的黏性。
表2 DIPP 的溶液性质
Table 2 Solution property of DIPP

?

图2 DIPP 尺寸排阻色谱图
Fig.2 Size exclusion chromatogram of DIPP
2.4 甲基化分析结果
表3为DIPP 的甲基化分析结果,糖残基类型为T-Glcp(29.8%),1,3-Glcp(42.6%)和1,3,6-Glcp(27.8%)(对应比例约为2∶3∶2)。这一比例与香菇多糖的相近[26-27],也与已有的竹荪β-葡聚糖的报道类似。在最早的关于竹荪葡聚糖的结构解析中得到的是具有(1→6)支链的(1→3)-β-D-葡聚糖,其糖残基Glcp-(1→、→3)-Glcp-(1→和→3,6)-Glcp-(1→的比值为1 ∶1.54 ∶0.99[28]。Wang等[29]也纯化得到此类型的竹荪β-葡聚糖。除β-葡聚糖外,Shi 等[25]还在棘托竹荪中得到以(1→6)为支链的α-(1→4)-葡聚糖。
表3 DIPP 糖苷键连接类型
Table 3 Linkage patterns analysis of DIPP

?糖苷键类型DIPP/%T-Glcp29.8 1,3-Glcp42.6 1,3,6-Glcp27.8
2.5 扫描电镜分析结果
图3是DIPP 的表面形貌。液氮急速冷冻使得DIPP 的多糖分子在溶液中的形态被固定,DIPP 呈丝状线性分布。
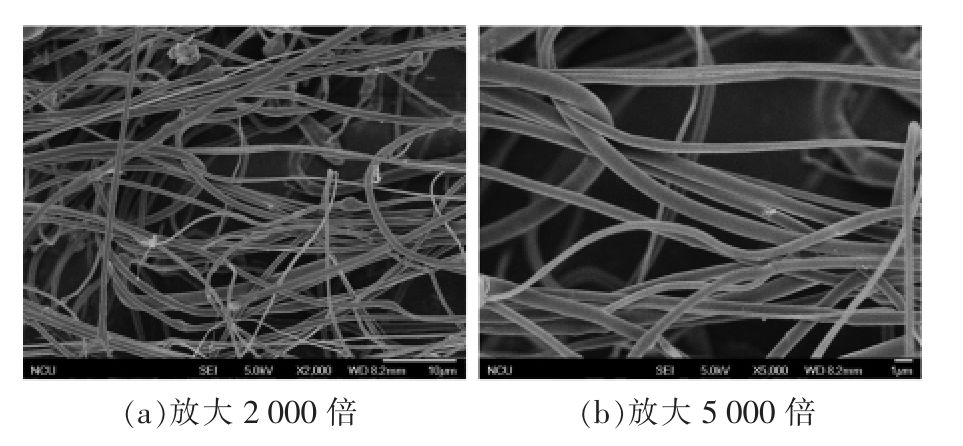
图3 DIPP 的扫描电镜图
Fig.3 SEM of DIPP
2.6 流变性质
图4显示不同浓度DIPP 表观黏度和成胶性能测试结果。DIPP 有剪切变稀的趋势,属于非牛顿流体。随着多糖浓度的增大,表观黏度也随之增强。与红托竹荪多糖相比[18],在相同质量分数下(质量分数为0.5%),DIPP 表观黏度要更大,而对比具有相似结构的香菇多糖,其表观黏度接近一致[30]。DIPP 质量分数为0.1%时,表现出溶胶性质〔储能模量(G')与损耗模量(G'')曲线有交叉〕,在更高浓度下,DIPP 的G' 值始终大于G'',表现出一定的成胶性能。
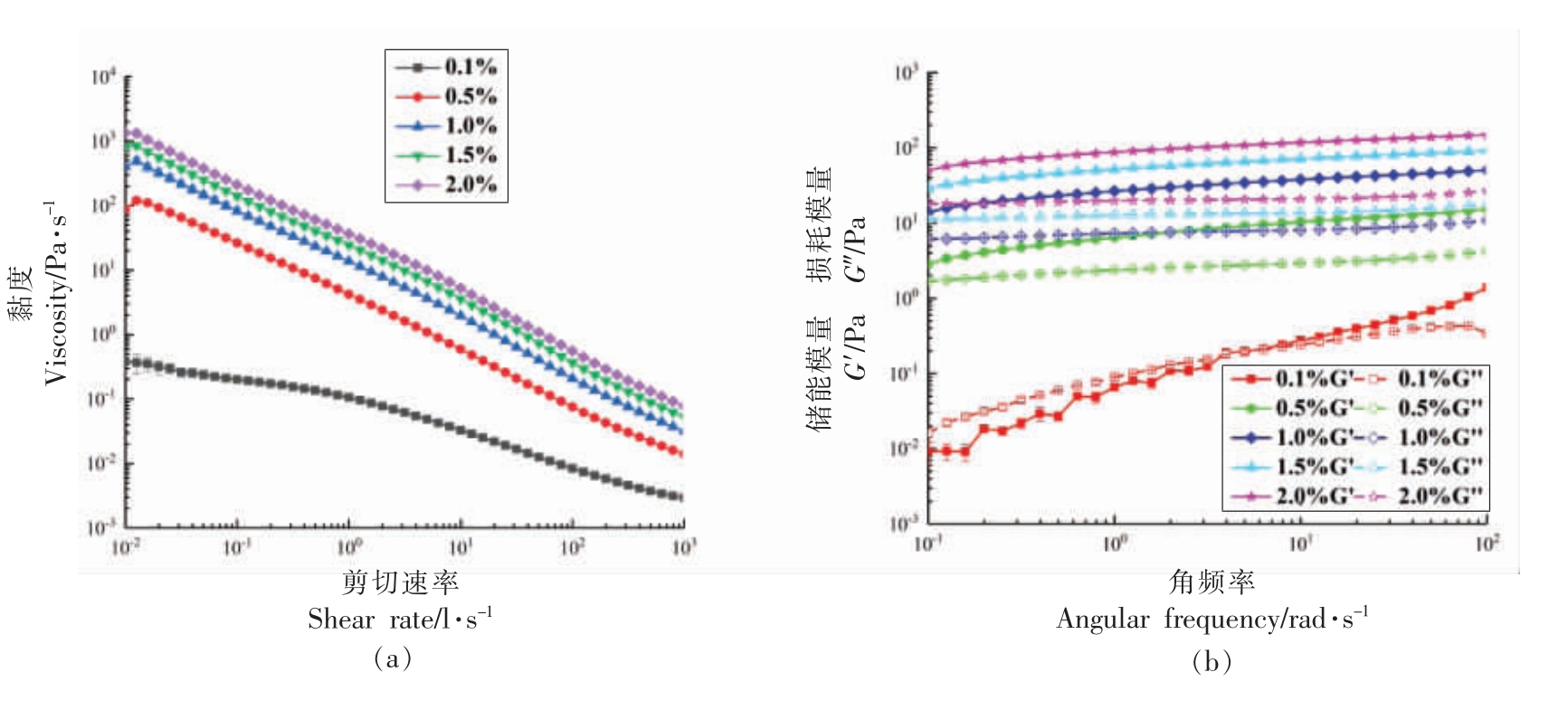
图4 浓度对DIPP 表观黏度(a)和凝胶特性(b)的影响
Fig.4 Effect of concentration on apparent viscosity (a) and gel properties (b) of DIPP
3 讨论与结论
从竹荪中提取纯化所得水溶性多糖DIPP 具有较高的分子质量,主要糖残基类型为T-Glap、1,3-Glcp 和1,3,6-Glcp,这与已报道的具有(1→6) 支链的 (1→3)-β-D-葡聚糖的糖残基类型一致。结合红外分析结果,确定DIPP 也是一种β-葡聚糖。HPSEC-MALLS 测定表明,DIPP 的特性黏度较高([η]=1 094.3 mL/g)。在对DIPP 的流变性的测定时也发现其黏性较强,具有弱凝胶性质,这与其结构有关。有研究发现,燕麦β-葡聚糖分子质量的增大对应黏度也会增大[31]。随着β-葡聚糖分子质量的降低,其黏度也随之降低[32],这表明在一定分子量范围,分子量与黏度呈正相关,凝胶强度与分子量的关系则相反,分子量越小,凝胶能力越强[33-34]。高分子量可能是导致DIPP 具有高黏性与弱凝胶性质的重要因素。此外,DIPP 的溶液性质也可能与其初级结构有关。1,3,6-Glcp 上存在支链位点,带有支链的多糖链在水中与羟基作用,形成分子间和分子内氢键,使其具备对应的溶液性质,其原理有待研究。
综上所述,DIPP 是一种β-葡聚糖,具有较高的黏度和一定的成胶性能。本研究结果为竹荪β-葡聚糖的功能活性提供了物质结构基础,也为竹荪多糖产品的开发和设计提供理论支持。
[1]BASHIR K M,CHOI J.Clinical and physiological perspectives of β-glucans:The past,present and future[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2017,18(9):1906.
[2]ZHU F M,DU B,XU B J.A critical review on production and industrial applications of beta-glucans[J].Food Hydrocolloids,2016,52:275-288.
[3]DU B,LIN C Y,BIAN Z X,et al.An insight into anti-inflammatory effects of fungal beta-glucans[J].Trends in Food Science & Technology,2015,41(1):49-59.
[4]LEI N,WANG M,ZHANG L F,et al.Effects of low molecular weight yeast β-glucan on antioxidant and immunological activities in mice[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2015,16 (9):21575-21590.
[5]ISHIMOTO Y,ISHIBASHI K,YAMANAKA D,et al.Production of low-molecular weight soluble yeast β-glucan by an acid degradation method[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,107:2269-2278.
[6]DU B,MEENU M,LIU H Z,et al.A concise review on the molecular structure and function relationship of β -glucan [J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2019,20(16):4032.
[7]WANG Y,HARDING S V,ECK P,et al.Highmolecular-weight β-glucan decreases serum cholesterol differentially based on the CYP7A1 rs3808607 polymorphism in mildly hypercholesterolemic adults[J].The Journal of Nutrition,2016,146(4):720-727.
[8]QIN Y Y,XIE J,XUE B,et al.Effect of acid and oxidative degradation on the structural,rheological,and physiological properties of oat β-glucan[J].Food Hydrocolloids,2021,112(8):106284.
[9]ZHANG Q Y,XIE J,XUE B,et al.Effect of sulfated modification on rheological and physiological properties of oat β-glucan oligosaccharides prepared by acid or oxidative degradation[J].Journal of Cereal Science,2021,99:103209.
[10]华洋林,高擎,唐健,等.不同产地竹荪营养成分的比较研究[J].食品工业科技,2011,32(10):418-420.HUA Y L,GAO Q,TANG J,et al.Study on comparison of nutritional components in fruiting bodies of Dictyophora indusiata from different regions[J].Science & Technology of Food Industry,2011,32(10):418-420.
[11]FU Y,LIN S,LU M,et al.Quantitative evaluation of ultrasound-assisted extraction of 1,3-β-glucans from Dictyophora indusiata using an improved fluorometric assay[J].Polymers,2019,11(5):864.
[12]KANWAL S,JOSEPH T P,ALIYA S,et al.Attenuation of DSS induced colitis by Dictyophora indusiata polysaccharide (DIP) via modulation of gut microbiota and inflammatory related signaling pathways[J].Journal of Functional Foods,2020,64:103641.
[13]WU D T,ZHAO Y X,GUO H,et al.Physicochemical and biological properties of polysaccharides from Dictyophora indusiata prepared by different extraction techniques[J].Polymers,2021,14(13):2357.
[14]吴定涛,巨瑶君,陆静峰,等.糖谱法比较不同产地竹荪多糖结构特征[J].食品科学,2014,35(13):98-102.WU D T,JU Y J,LU J F,et al.Characterization and comparison of polysaccharides from Dictyophora indusiata using saccharide mapping[J].Food Science,2014,35(13):98-102.
[15]DUBOIS M,GILLES K A,HAMILTON J K,et al.Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances[J].Analytical Chemistry,1956,28(3):350-356.
[16]BRADFORD M M.A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein -dye binding [J].Analytical Biochemistry,1976,72(1/2):248-254.
[17]WANG Y,ZHANG T,XIN Y,et al.Comprehensive evaluation of alkali -extracted polysaccharides from Agrocybe cylindracea:Comparison on structural characterization [J].Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,255:117502.
[18]WANG Y X,YIN J Y,HUANG X J,et al.Structural characteristics and rheological properties of high viscous glucan from fruit body of Dictyophora rubrovolvata[J].Food Hydrocolloids,2020,101:105514.
[19]CHEN J C,ZHANG X,HUO D,et al.Preliminary characterization,antioxidant and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities of polysaccharides from Mallotus furetianus[J].Carbohydrate Polymers,2019,215:307-315.
[20]SU Y,LI L.Structural characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from four auriculariales[J].Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,229:115407.
[21]DENG C,HU Z,FU H T,et al.Chemical analysis and antioxidant activity in vitro of a β-D-glucan isolated from Dictyophora indusiata[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2012,51(1/2):70-75.
[22]XIAO H,CHEN C,LI C,et al.Physicochemical characterization,antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities of selenized polysaccharides from Sargassum pallidum[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,132:308-315.
[23]AHMAD A,ANJUM F M,ZAHOOR T,et al.Extraction and characterization of β-D-glucan from oat for industrial utilization[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2010,46(3):304-309.
[24]HE P,HE L,ZHANG A,et al.Structure and chain conformation of a neutral polysaccharide from sclerotia of Polyporus umbellatus[J].Carbohydrate Polymers,2017,155:61-67.
[25]SHI X,LI O,YIN J,et al.Structure identification of α -glucans from Dictyophora echinovolvata by methylation and 1D/2D NMR spectroscopy[J].Food Chemistry,2019,271:338-344.
[26]SAITÔ H,OHKI T,TAKASUKA N,et al.A 13CN.M.R.-Spectral study of a gel-forming,branched(1→3)-β-D-glucan,(lentinan) from lentinus edodes,and its acid-degraded fractions.Structure,and dependence of conformation on the molecular weight[J].Carbohydrate Research,1977,58(2):293-305.
[27]SAITÔ H,OHKI T,SASAKI T.A 13C-nuclear magnetic resonance study of polysaccharide gels.Molecular architecture in the gels consisting of fungal,branched (1→3)-β-D-glucans (lentinan and schizophyllan) as manifested by conformational changes induced by sodium hydroxide[J].Carbohydrate Research,1979,74(1):227-240.
[28]HARA C,KIHO T,UKAI S.A branched (1→3)-β-D-glucan from a sodium carbonate extract of Dictyophora indusiata fisch[J].Carbohydrate Research,1983,117:201-213.
[29]WANG J T,XU X J,ZHENG H,et al.Structural characterization,chain conformation,and morphology of a β-(1→3)-D-glucan isolated from the fruiting body of Dictyophora indusiata[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2009,57(13):5918-5924.
[30]XU X J,XU J,ZHANG Y Y,et al.Rheology of triple helical lentinan in solution:Steady shear viscosity and dynamic oscillatory behavior[J].Food Hydrocolloids,2008,22(5):735-741.
[31]KIM H J,WHITE P J.Impact of the molecular weight,viscosity,and solubility of β-glucan on in vitro oat starch digestibility[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2013,61(13):3270-3277.
[32]BYUN E,KIM J,SUNG N,et al.Effects of gamma irradiation on the physical and structural properties of β-glucan[J].Radiation Physics and Chemistry,2008,77(6):781-786.
[33]LI W,CUI S W,KAKUDA Y.Extraction,fractionation,structural and physical characterization of wheat β-D-glucans[J].Carbohydrate Polymers,2006,63(3):408-416.
[34]LI W,CUI S W,WANG Q,et al.Studies of aggregation behaviours of cereal β-glucans in dilute aqueous solutions by light scattering:Part I.Structure effects[J].Food Hydrocolloids,2011,25(2):189-195.